Ultimate Web Hosting Guide: Key Insights & Tips
I. Introduction to Web Hosting
In today’s digital age, selecting the right web hosting service providers is critical to the success of your website. For any business entity or a developer hosting is a massive key thing that will dictate the success of your online business.
With this final web hosting guide, the aim is to help you understand all you need to know about web hosting including the different kinds, and the essential features to consider. So, let’s start by knowing more about the world of web hosting and help you make the right choices!
Are you excited about learning web hosting?🤩

So, let’s get started.
What is Web Hosting?
Web hosting is a service that allows individuals and organizations to host their website on a server, making it accessible to the public via the Internet.
In simple terms, web hosting is like renting a piece of land on the internet where you can build your website. When you sign up for a web hosting service, you’re essentially renting space on a server—a powerful computer that stores all the files, images, and data that make up your website. This means that when someone types in your website’s address, their browser can find your site and display it for them to see.
I remember the first time I tried to set up my own website. I had this grand idea for a blog but was completely clueless about where to start. After some research, I discovered that without web hosting, my blog would be like a house without land—it simply wouldn’t exist online! So, I took the plunge and signed up with a hosting provider.
Purpose of Web Hosting
The primary purpose of web hosting is to ensure that your website is accessible to anyone with an internet connection. It provides the infrastructure necessary for your site to function correctly. This includes:
- Storing Website Files: All your website's files need to be stored somewhere, and that's what web hosting does.
- Making Your Site Accessible: The hosting provider ensures that when someone types in your domain name, they can access your site without any hiccups.
- Providing Security: Good web hosts implement security measures to protect your data from breaches or attacks.
How Web Hosting Works?
So, how does this all work behind the scenes? Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Domain Name: First, you need a domain name (like www.yoursite.com). This is the address people will use to find your website.
- Server Connection: When someone enters your domain name into their browser, the browser translates that name into an IP address (a unique identifier for each server).
- File Retrieval: The browser sends a request to the server where your website is hosted, asking for the files needed to display your site.
- Loading Your Site: The server responds by sending those files back to the browser, which then displays your website.
I remember feeling amazed when I first saw my blog live on the internet! It felt like magic—just a few clicks and my thoughts were out there for everyone to see.
Why Web Hosting is Important?
Understanding why web hosting is vital can help you make informed decisions about choosing the right service for your needs. Here are some key reasons:
- Performance: A good web host ensures that your site loads quickly and runs smoothly. Slow sites can frustrate visitors and lead them to leave before they even see what you have to offer.
- Reliability: You want a host that guarantees uptime—meaning your site is available most of the time. If your site goes down frequently, you could lose visitors and credibility.
- Support: If something goes wrong (and it will at some point), having reliable customer support can save you hours of stress and confusion.
II. Types of Web Hosting
(i) Shared Hosting
Let's talk about shared hosting, the most popular web hosting option out there. I'm excited to break it down for you in simple terms.

Image credit: Inmotion Hosting
What is Shared Hosting?
Shared hosting is like renting an apartment in a big building. You have your own space (your website), but you share the building (the server) with many other tenants (other websites). This setup makes shared hosting one of the most cost-effective options available for hosting your website. You can get started for as little as $1 to $20 a month, which is perfect for bloggers, small businesses, and anyone just starting their online journey
In simple words, with shared hosting, multiple websites are stored on a single server. This means that all users share the server's resources—like CPU power, RAM, and disk space. The beauty of this arrangement is that it significantly reduces costs. Just like splitting rent with roommates makes living expenses more manageable, shared hosting divides server costs among user
How Does Shared Hosting Work?
So, how does this all work? Shared hosting works by having multiple websites share a physical server, with each website allocated its own virtual server and resources like CPU, RAM, and storage. The websites don't interact with each other, and when a visitor accesses a website, their browser sends a request to the shared server, which then directs them to the website's files.
Imagine you’re on a cruise ship. Everyone shares the same vessel (the server) but has their own cabins (websites). You all enjoy the same amenities while having unique experiences. Similarly, in shared hosting, while you share server resources with others, your website remains distinct and separate from theirs.
Advantages of Shared Hosting
When I first started my journey into web hosting, I quickly realized that shared hosting was a fantastic option for someone like me—someone who was just getting their feet wet in the digital world. As I explored this option further, I discovered alot of advantages that made shared hosting appealing. Let’s dive into some of these benefits together!
1. Affordable
One of the biggest draws of shared hosting is its affordability. When I launched my first blog, I was on a tight budget. With plans often starting as low as $1 to $10 per month, shared hosting allowed me to get my website up and running without emptying my wallet. This financial flexibility is especially beneficial for students, freelancers, or anyone just starting out.
2. Accessible
Shared hosting is incredibly accessible. Most providers offer various plans that cater to different needs and budgets. This means you can find something that fits your requirements without feeling overwhelmed by choices. When I first signed up, I appreciated how easy it was to navigate the options available.
3. Provides Security
While security might not be the first thing that comes to mind when you think of shared hosting, many providers include robust security features in their packages. They often offer firewalls, malware scanning, and regular backups. I remember feeling relieved knowing that my blog was protected, even if it was just a small space on a shared server.
4. Scalability
As my blog grew, so did my needs. Shared hosting offers scalability options that allow you to upgrade your plan as your traffic increases or as you add more features. This flexibility means you won’t have to migrate your site to a new server right away; you can simply adjust your plan as necessary.
5. Excellent Customer Service
Most reputable shared hosting providers offer excellent customer service. When I had questions about setting up my email accounts or needed help with a technical issue, I found their support teams to be responsive and helpful. Whether through live chat, email, or phone support, having access to knowledgeable staff made a significant difference.
6. Easy-to-Use and User-Friendly
If you’re not particularly tech-savvy (like me!), you’ll appreciate the user-friendly interfaces that come with shared hosting plans. Most providers use intuitive control panels that make managing your website a breeze. I remember being able to install WordPress with just a few clicks—no coding required!
7. Enables Multiple Domains
Another fantastic feature of shared hosting is the ability to host multiple domains under one account. This means if you have several projects or blogs (which I eventually did), you can manage them all from one place without needing separate hosting accounts for each one.
8. Ideal for Small Projects
If you're working on small projects or personal websites, shared hosting is often the perfect fit. It provides all the necessary features without overwhelming you with unnecessary resources. My first blog was a small project focused on sharing recipes, and shared hosting was more than enough for my needs at the time.
9. Beginner Friendly
For anyone new to web hosting, shared hosting is incredibly beginner-friendly. The setup process is straightforward and typically involves just a few steps—selecting your plan, registering your domain (if needed), and installing any necessary software like WordPress or Joomla.
10. No Technical Expertise Required
You don’t need to be a tech guru to manage a website on shared hosting! Most providers offer tools and resources that guide you through every step of the process. I remember feeling empowered knowing that I could handle things myself without needing extensive technical knowledge.
11. Straightforward Setup
Setting up shared hosting is usually quick and painless. After signing up, you’ll receive instructions on how to get started right away—often within minutes! The last thing I wanted was to spend hours figuring things out before even launching my site.
12. Effortless Maintenance
One of the best parts about shared hosting is that maintenance is largely taken care of for you by the provider. They handle server updates, security patches, and other technical tasks so you can focus on what really matters: creating content and engaging with your audience.
Disadvantages of Shared Hosting
While shared hosting can be a great starting point for many website owners, it’s not without its drawbacks. As I navigated my own web hosting journey, I encountered several disadvantages that are important to consider before diving into a shared hosting plan. Let’s explore these potential pitfalls together.
1. No Root Access
One of the first things I noticed was the lack of root access. This means you don’t have complete control over the server. For someone like me who enjoys tinkering and customizing, this was a bit frustrating. Without root access, you can’t install custom software or make significant changes to server settings, limiting your ability to optimize your site fully.
2. Technical Restrictions
Shared hosting comes with its fair share of technical restrictions. For instance, many providers limit the types of scripts and applications you can run. I remember wanting to experiment with specific plugins for my blog but finding out that they weren’t supported on my shared plan. This can be a real bummer if you have particular needs for your website.
3. Performance and Security Concerns
Performance can be a significant issue in shared hosting environments. Since multiple websites share the same resources, if one site experiences a traffic spike or runs resource-heavy applications, it can slow down the entire server. I experienced this firsthand when my blog's load times increased dramatically after another site on the same server got popular overnight.
4. Decreased Site Speed
Speaking of performance, decreased site speed is another drawback. If your neighbor's website is hogging resources, your site may suffer as a result. Slow loading times can frustrate visitors and negatively impact your search engine rankings. I learned this lesson the hard way when my blog's traffic dropped because users were abandoning my site due to slow speeds.
5. Potential Server Crashes
Shared servers are prone to crashes if one website experiences issues or traffic surges. This can lead to downtime for all sites hosted on that server, including yours. I remember one particularly stressful day when my blog went down because another site was hit by a sudden influx of visitors, leaving me scrambling to reassure my readers.
6. Limited Resources
With shared hosting, you’re sharing resources like CPU power, RAM, and bandwidth with other websites. This limitation means that as your site grows and attracts more visitors, you may quickly outgrow your shared plan. I found myself hitting resource limits sooner than expected, which pushed me to consider upgrading sooner than I had planned.
7. Shared IP Address
Another downside is that you share an IP address with other websites on the server. If one of those sites engages in spammy or unethical practices, it could potentially harm your site's reputation and SEO rankings. It’s a risk that many don’t consider until it’s too late—something I wish I had been more aware of at the start.
8. Limited Customization
Customization options are often limited with shared hosting plans. You typically have to stick to pre-approved software and configurations set by the hosting provider. This lack of flexibility can be frustrating if you want to tailor your website’s environment to fit specific needs or preferences.
9. Limited Capacity for Growth
While shared hosting is suitable for small projects and beginner websites, it may not accommodate significant growth over time. If your site begins to gain traction and attract more visitors than anticipated, you might find yourself needing to migrate to a different type of hosting sooner than expected—something I had to do after just a few months.
Who Should Use Shared Hosting?
Shared hosting is an excellent fit for a specific group of website owners. Here are some scenarios where shared hosting shines:
1. Beginners and First-Time Website Owners
If you’re just starting out and have little to no technical expertise, shared hosting is a fantastic option. It’s designed to be user-friendly, allowing you to focus on creating content rather than getting bogged down in technical details. I remember when I first launched my blog; I was relieved by how easy it was to set up my site without needing to know much about servers or coding.
2. Small Businesses and Personal Blogs
For small businesses or personal blogs that don’t expect high traffic initially, shared hosting offers an affordable way to establish an online presence. You can get started with minimal investment, which is crucial for many small business owners. When I started my blog about cooking, I didn’t have a big budget, and shared hosting allowed me to get my ideas out into the world without financial stress.
3. Websites with Low to Moderate Traffic
If your website is expected to have low to moderate traffic levels, shared hosting can handle this without issue. It’s perfect for sites that don’t require extensive resources or high performance. I found that my initial traffic was manageable on a shared plan, making it a great starting point.
4. Temporary Projects
If you’re working on a temporary project or a short-term campaign, shared hosting can be a cost-effective solution. You can easily set up your site and take it down when you’re done without worrying about long-term commitments.
5. Budget-Conscious Users
For those who are budget-conscious but still want a reliable web presence, shared hosting is often the most economical option available. With prices typically ranging from $2.99 to $9.99 per month, it allows you to allocate funds toward other aspects of your project.
How Do You Choose the Right Hosting Provider?
Choosing the right hosting provider can feel overwhelming with so many options available. Here are some tips based on my experiences and insights from industry experts:
1. Assess Your Needs
Before diving into the selection process, take some time to assess your needs. Consider factors like expected traffic levels, the type of website you’re building (blog, e-commerce, portfolio), and any specific features you might require (like email accounts or SSL certificates). This will help narrow down your options.
2. Look for Reliability and Uptime Guarantees
A reliable hosting provider should offer strong uptime guarantees—ideally 99.9% or higher. Downtime can hurt your site’s reputation and lead to lost visitors or sales. I learned this the hard way when my initial host had frequent outages; it was frustrating for both me and my readers.
3. Check Customer Support Options
Good customer support is crucial, especially if you’re new to web hosting. Look for providers that offer multiple support channels—like live chat, email, and phone support—so you can get help when you need it most. I found that having responsive customer support made all the difference when I encountered issues early on.
4. Read Reviews and Testimonials
Take some time to read reviews and testimonials from other users. This can give you insights into the provider’s performance and reliability from real-world experiences. I often turned to forums and review sites when researching my options.
5. Evaluate Pricing Plans
While cost is an important factor, don’t just go for the cheapest option available; consider what features are included in each plan. Some providers may offer promotional rates that increase significantly after the first year, so be sure to check renewal rates as well.
6. Look for Scalability Options
As your website grows, you may need more resources than what shared hosting can provide. Choose a provider that offers easy upgrade paths so you can transition smoothly if needed. This flexibility was key for me as my blog began attracting more visitors.
5 Best Shared Hosting Services Provider
| NO. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bluehost | $2.95/mo | Free Domain, Unlimited Storage, Unlimited Bandwidth | 4.9/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | Hostinger | $1.99/mo | Free Domain, Unlimited Storage, Unlimited Bandwidth | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | Interserver | $2.50/mo | Unlimited Storage, Unlimited Bandwidth, Free SSL | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | Namecheap | $2.88/mo | Free Domain, Unlimited Storage, Unlimited Bandwidth | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | Cloudways | $10.00/mo | Free SSL, Unlimited Storage, Unlimited Bandwidth | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
(ii) VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server)
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) is a powerful solution for anyone looking to host applications or websites with more control and flexibility than shared hosting can offer. Essentially, a VPS is a virtual machine that runs its own operating system and provides dedicated resources from a physical server.
This means you can enjoy the benefits of having your own server while still sharing the underlying hardware with other users. Let’s dive into what VPS is, its uses, and why it might be the right choice for you.
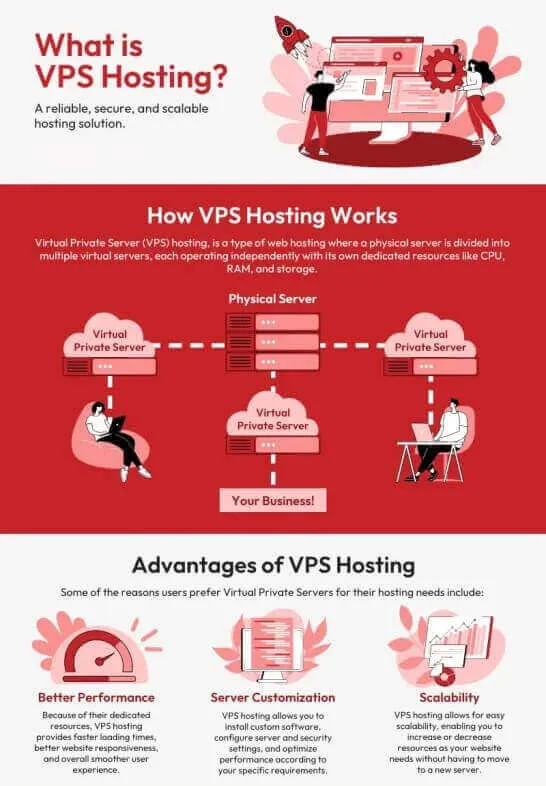
Image credit: Inmotion Hosting
What is VPS hosting?
A VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a type of web hosting that provides a virtualized server environment, offering dedicated resources, privacy, and control, bridging the gap between shared hosting and dedicated servers.
A VPS is like having your own apartment in a large building. You share the building with others, but your apartment is yours to customize as you see fit. You have dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage, which are allocated specifically to you. This setup allows for greater performance and stability compared to shared hosting, where multiple websites compete for the same resources.
When I first learned about VPS hosting, I was amazed at how it could bridge the gap between shared and dedicated hosting. It provides the flexibility of a dedicated server without the hefty price tag. I remember setting up my first VPS; it felt empowering to have complete control over my environment. I could install software, configure settings, and optimize performance based on my specific needs.
What is a VPS used for?
VPS hosting is incredibly versatile and can be used for various purposes. Here are three primary uses that I've found particularly beneficial:
1. Launch web applications
One of the primary uses of a VPS is to launch and run web applications. For instance, if you're developing an e-commerce site or a content management system (CMS), a VPS provides the necessary resources to ensure smooth operation.
I recall when I decided to create a web-based project management tool; using a VPS allowed me to handle increased traffic during peak times without any hiccups. With a VPS, you can easily scale your resources as your application grows.
If you expect high traffic during special promotions or events, you can upgrade your plan without significant downtime. This flexibility has been invaluable for my projects, such as when I launched a popular online course platform and needed to quickly scale to accommodate a surge in enrollments.
2. Build test environments
Another significant advantage of using a VPS is the ability to create test environments for development purposes. When working on new features or updates for my e-commerce site, I often set up a separate VPS to test changes before deploying them live. This way, if something goes wrong—like breaking the payment gateway—I can troubleshoot without affecting my main website's functionality.
For example, I once experimented with different integrations and APIs on my test VPS. It allowed me to see how they would perform without risking my live site's stability. This practice not only saved me time but also provided peace of mind knowing that my main site was safe from potential errors, such as a faulty checkout process or compromised customer dat
3. Secondary storage
A VPS can also serve as secondary storage for data files, acting as a secure location for important documents, images, or backups. For instance, I use my VPS as a centralized hub for all my critical files. It acts like my personal cloud storage solution where I can access data from anywhere while ensuring it's protected from unauthorized access.
Setting up automated backups on my VPS has been another lifesaver; I no longer worry about losing important content due to accidental deletions or system failures.
How does VPS hosting compare to other types of hosting?
When considering web hosting options, it’s essential to understand how VPS hosting compares to other types of hosting, such as shared and dedicated hosting.
Each option has its unique benefits and drawbacks, depending on your specific needs and the level of control you require. Let’s break down these hosting types to help you make an informed decision.
1. Shared hosting
Shared hosting is often the first step for many website owners due to its affordability. In this setup, multiple websites share a single physical server and its resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage. While this can be a cost-effective solution for small websites or blogs with low traffic, it comes with significant limitations.
I remember when I started my first blog on a shared hosting plan. Initially, it was perfect for my needs—simple, cheap, and easy to set up. However, as my blog began to gain traction and traffic increased, I quickly noticed performance issues. My site would slow down during peak times, and I even faced downtime because other sites on the same server were hogging resources. It was frustrating!
The downside of shared hosting is that you have no control over the server environment. If another website experiences a surge in traffic or a technical issue, it can directly affect your site’s performance. Plus, security vulnerabilities from neighboring sites can pose risks to your own website.
2. Dedicated hosting
On the opposite end of the spectrum is dedicated hosting. With this option, you rent an entire physical server exclusively for your website. This means you have complete control over the server’s resources and configurations without having to share them with anyone else.
While dedicated hosting offers superior performance and reliability—ideal for large enterprises or high-traffic websites—it comes at a significantly higher cost. However, the price tag was daunting! It felt like renting an entire house when all I needed was a bigger apartment.
Dedicated hosting is like having your own private office: spacious and comfortable but often more than what you need if you're just starting out or running a small business.
3. VPS hosting vs. shared hosting vs. dedicated hosting
In VPS hosting, resources are allocated specifically to each virtual server instance. This means that even though you’re sharing hardware with others, you won’t experience performance issues caused by neighboring websites.
To visualize this comparison:
| Feature | Shared Hosting | Dedicated Hosting | VPS Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | High | Moderate |
| Resource Allocation | Shared among all users | Exclusive access | Dedicated portion of resources |
| Performance | Can be slow during peak times | High and consistent | Reliable with minimal fluctuation |
| Control | Limited | Complete | Moderate |
| Security | Vulnerable due to shared resources | High security | Isolated from other users |
What are the types of VPS hosting?
When it comes to VPS hosting, understanding the different types available can help you choose the right plan for your needs. Each type of VPS offers varying levels of management, control, and customization, catering to different user requirements.
Let’s explore the three main types of VPS hosting: unmanaged, managed, and semi-managed.
1. Unmanaged VPS hosting
Unmanaged VPS hosting is the most basic type of VPS service available. As the name suggests, this option places the responsibility of server management entirely on you.
This means you have full control over your virtual server, including the ability to install software, configure settings, and handle security measures.
For those who are tech-savvy or have a dedicated IT team, unmanaged VPS can be an excellent choice. For instance, a web development agency can benefit from unmanaged VPS hosting, as it allows them to customize server configurations to meet specific project requirements, resulting in optimal performance and security.
However, it requires a solid understanding of server management, much like a master chef needs to know their way around a commercial kitchen to craft the perfect dish.
This type of hosting is ideal for developers or businesses looking for maximum flexibility and control over their environment. However, if you’re not comfortable with managing technical tasks, you might find it overwhelming.
2. Managed VPS hosting
On the other hand, managed VPS hosting offers a more hands-off approach. With this type of service, your hosting provider takes care of all the day-to-day management tasks associated with your server. This includes software updates, security patches, backups, and monitoring.
The convenience of managed VPS hosting is a significant advantage for those who want to focus on their core business activities without worrying about server maintenance.
For example, an e-commerce company can benefit from managed VPS hosting, as it enables them to focus on product development, marketing, and customer service, while their provider handles server security, updates, and performance optimization.
This way, they can ensure a smooth and secure online shopping experience for their customers, without dedicating resources to server management.
Managed VPS is perfect for individuals or small businesses that may not have the technical expertise or time to manage a server themselves. It combines the benefits of dedicated resources with professional support, making it an attractive option for many users.
3. Semi-managed VPS hosting
Semi-managed VPS hosting strikes a balance between unmanaged and managed options. In this setup, your hosting provider takes care of critical infrastructure tasks—like hardware maintenance and network management—while you retain control over certain aspects of your server environment, such as software installation and configuration.
This middle ground is ideal for users who have some technical knowledge but may not want to handle every aspect of server management. Let me explain it with an example, a growing startup can benefit from semi-managed hosting, as it offers the perfect balance of control and support.
They can customize their applications and have root access, while still relying on their provider for critical tasks such as security updates, backups, and network monitoring. This way, they can focus on developing their product and expanding their business without being bogged down by server management responsibilities.
Semi-managed VPS is suitable for businesses that want flexibility in their server environment but may not have the resources for full management or the expertise for complete self-management.
Is VPS hosting secure?
Yes, VPS hosting is generally secure, offering a high level of isolation, dedicated resources, and robust security features. Each VPS operates in an isolated environment, which means that vulnerabilities in one server do not affect others. This isolation provides a layer of protection against common threats like malware and DDoS attacks.
However, while VPS environments are inherently more secure, they are not immune to breaches. It's essential to implement robust security measures to protect your data. For example, a web development agency can enhance their server's security posture by changing default SSH ports, using strong passwords, and regularly updating their software.
Additionally, implementing a firewall, monitoring server activity, and performing regular security audits can help identify and address potential vulnerabilities. By taking these proactive measures, agencies can safeguard their clients' sensitive data and maintain the integrity of their online applications.
To further bolster security, consider employing additional strategies such as:
- Using firewalls: A properly configured firewall can block unauthorized access and protect against various types of attacks.
- Regular monitoring: Keeping an eye on server logs can help you detect unusual activities early on.
- Implementing backups: Regular backups ensure that you can restore your data in case of an attack or failure.
By taking these proactive steps, you can create a secure environment for your applications and data.
Is VPS hosting fast and reliable?
Speed and reliability are critical factors for any website or application. VPS hosting typically offers better performance compared to shared hosting because resources are dedicated to your virtual server. This means that during traffic spikes or high-demand periods, your site is less likely to slow down or crash.
For example, an e-commerce website can benefit greatly from VPS hosting, as it ensures that the site can handle high traffic volumes during sales or promotional events without compromising performance. This reliability is essential for maintaining customer trust, improving SEO rankings, and ultimately driving business growth.
Moreover, many VPS providers offer high uptime guarantees—often around 99.9%—which means your website will be available when users need it most. This level of reliability is especially important if you're running an e-commerce site or any platform where downtime can lead to lost revenue.
Factors Contributing to Speed and Reliability:
- Dedicated Resources: With VPS hosting, you have dedicated CPU, RAM, and storage that aren’t shared with other users.
- Scalability: As your website grows, you can easily upgrade your resources without significant downtime.
- Optimized Performance: Many VPS providers offer performance optimization features like caching solutions that enhance loading times
Advantages of VPS Hosting
When considering VPS hosting, it’s essential to understand the various advantages it brings to the table. From easy customization to enhanced security, VPS hosting offers a range of benefits that cater to different needs and budgets. Let’s explore these advantages in detail.
1. Easy Customization
One of the standout features of VPS hosting is the level of customization it offers. Unlike shared hosting, where you’re limited by the provider’s settings, VPS allows you to configure your server environment according to your specific needs.
I remember when I first switched to VPS; I was thrilled to discover how easily I could install custom software and applications. This flexibility meant I could optimize my server for performance and security without any restrictions. Whether you need a specific version of PHP or want to run a particular application, VPS hosting gives you the control to tailor your environment.
Many VPS providers offer user-friendly control panels that simplify the management process, making it easy even for those with limited technical expertise.
2. Higher Security
Security is a critical concern for any online business, and VPS hosting provides enhanced security compared to shared hosting environments. Since each VPS operates in isolation, your server resources are not shared with other users, which significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
For example, when I transitioned to VPS hosting, I felt a sense of relief knowing that my data was better protected. Many providers also offer additional security features such as DDoS protection and firewalls, which further safeguard your server from potential threats.
Implementing regular security updates and monitoring can help maintain a secure environment, allowing you to focus on growing your business without worrying about vulnerabilities.
3. VPS Web Hosting Prices
When it comes to VPS web hosting prices, this option often strikes a balance between affordability and performance. While dedicated servers can be expensive, VPS hosting provides many of the same benefits at a fraction of the cost.
For example, some VPS plans start as low as $4.99 per month, making them accessible for startups and small businesses. This pricing structure allows you to enjoy dedicated resources like CPU and RAM without breaking the bank.
Moreover, as your business grows, you can easily scale up your resources without incurring significant costs. This scalability is crucial for managing fluctuating traffic levels while keeping your budget in check.
4. Maintenance and Access to the Server
With VPS hosting, you typically have full root access to your server, allowing you to manage maintenance tasks effectively. This means you can perform updates, install software, and configure settings according to your requirements.
I found this aspect particularly beneficial when I wanted to optimize my server’s performance; having root access allowed me to make changes quickly without waiting for support from my hosting provider.
While some users prefer managed VPS options—where the provider handles maintenance tasks—having the ability to manage your server can be empowering for those with technical knowledge. You can choose the level of management that suits your needs best.
5. Technical Requirements
While VPS hosting offers many advantages, it’s essential to consider the technical requirements involved in managing a virtual private server. If you opt for unmanaged VPS hosting, you'll need a solid understanding of server management and administration.
For those who may not be as technically inclined, managed or semi-managed options are available that provide varying levels of support while still allowing for customization. This flexibility ensures that you can find a plan that meets both your technical capabilities and business needs.
Disadvantages of VPS Hosting
While VPS hosting offers numerous advantages, it also comes with its own set of disadvantages that potential users should consider. Understanding these drawbacks can help you make an informed decision about whether VPS is the right fit for your needs.
Let’s explore some of the main disadvantages of VPS hosting
1. Budget
One of the most significant drawbacks of VPS hosting is the cost. While it is generally more affordable than dedicated hosting, at the same time it is still more expensive than shared hosting if you’re just getting started or have a limited budget.
2. Server Management
With great power comes great responsibility! While VPS hosting gives you more control over your server environment, it also means you are responsible for managing it. If you choose an unmanaged VPS plan, you’ll need to handle everything from software updates to security configurations.
If you're not technically inclined or lack the time to manage a server, this could become a significant disadvantage.
For those who prefer less responsibility, managed VPS hosting is an option, but it typically comes at a higher price point.
3. Technical Issues
If you're handling your VPS Hosting yourself, make sure you set it up correctly. Otherwise, your website will be more vulnerable to security threats.
If you're not prepared to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues as they arise, you might find VPS hosting to be more challenging than expected.
4. Operating System Selection Difficulty
Choosing the right operating system for your VPS can also present challenges. Unlike shared hosting, where the provider typically manages the environment for you, with VPS hosting, you often have to select and configure your operating system yourself.
This can be daunting if you're unfamiliar with different OS options like Linux distributions or Windows Server. Each operating system has its own set of features and compatibility considerations that can impact your applications and overall performance.
For example, I initially struggled with selecting the right Linux distribution for my server. After some trial and error—and a few frustrating hours—I finally found a setup that worked well for my needs. However, this experience taught me that careful consideration is essential when choosing an operating system for your VPS.
Why should you choose VPS?
- Dedicated Resources: Get allocated CPU, RAM, and storage for optimal performance.
- Flexibility & Control: Customize your server to meet specific needs.
- Scalability: Easily upgrade or downgrade resources as your needs change.
- Security: Enjoy enhanced security features and isolation from other users.
- Reliability: Experience fewer downtime issues and faster loading speeds.
When should you switch to VPS hosting?
Switching to VPS hosting can be a game-changer for many website owners. If you’re currently using shared hosting or feeling constrained by your current setup, it might be time to consider making the switch. Here are some key indicators that suggest it’s time to upgrade to a VPS.
1. Handle more website traffic
One of the most compelling reasons to switch to VPS hosting is the need to handle increased website traffic. If your site is experiencing more visitors than it can manage—resulting in slow load times or even crashes—VPS hosting can provide the dedicated resources necessary to accommodate that growth.
I remember when my blog started gaining traction; I was on a shared hosting plan at the time. Suddenly, my site was getting more traffic than I anticipated, and it felt like I was trying to run a marathon in flip-flops! The slow loading times were frustrating for my visitors, and I knew I needed a solution. Upgrading to VPS allowed me to scale up resources like CPU and RAM, which made a noticeable difference in performance.
With VPS hosting, you’re allocated specific resources that aren’t shared with other users, meaning your site can handle spikes in traffic without sacrificing speed or reliability. This is especially important if you run an e-commerce site or any platform where user experience is crucial.
2. Customize applications
Another significant advantage of VPS hosting is the ability to customize applications and server configurations. Unlike shared hosting, where you’re often limited by the provider's settings, VPS gives you the freedom to install software and tailor your environment according to your needs.
For instance, when I transitioned to VPS, I wanted to implement specific caching mechanisms and security protocols that weren’t available on my previous plan. With root access, I could install and configure everything exactly how I wanted it. This level of customization not only improved my site's performance but also enhanced its security profile.
If you have specific applications or software requirements, VPS hosting allows you to create an environment that supports those needs without compromise.
3. Reduce server errors
Frequent server errors can be a major headache for website owners. If you find yourself constantly dealing with downtime or error messages due to resource limitations on shared hosting, it’s time to consider switching to VPS.
With dedicated resources in a VPS environment, you significantly reduce the chances of encountering server errors caused by other users on the same server. This was a major relief for me after moving from shared hosting; my website's uptime improved dramatically.
In fact, many VPS providers offer high uptime guarantees—often around 99.9%—which means you can trust that your site will be available when your visitors need it most. This reliability is essential for maintaining user trust and improving SEO rankings.
4. You’re On A Budget
You might think that upgrading to VPS hosting would break the bank, but that's not necessarily true! In fact, VPS hosting often strikes a perfect balance between cost and performance, making it an excellent choice for those on a budget.
Many businesses find that VPS hosting offers a cost-effective solution for growing their online presence. For instance, e-commerce websites can benefit from VPS hosting's dedicated resources, ensuring smooth performance during peak shopping seasons, without the need for expensive dedicated servers. Some providers offer plans starting as low as $5 per month!
Moreover, with VPS hosting, you get more value for your money: dedicated resources mean better performance without needing to invest in an expensive dedicated server right away. This cost-effectiveness allows you to allocate funds elsewhere in your business while still enjoying superior hosting capabilities.
Top 5 VPS Hosting Providers
| Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hostinger | Starting at $4.99/mo | 4 GB RAM, 50 GB NVMe disk space, 4 TB bandwidth, Free weekly backups | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| Digital Ocean | Starting at $4/mo | 1 GB RAM, 25 GB SSD, 1 TB transfer, Scalable Droplets | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| IONOS | Starting at $2/mo | 1 vCore, 1 GB RAM, 10 GB NVMe, Unlimited traffic, Free Plesk Web Host Edition | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| Ultahost | Starting at $3.29/mo | Unlimited bandwidth, SSD storage, 100% uptime, Managed plans | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| HostGator | Starting at $19.95/mo | 2 GB RAM, 120 GB disk space, 1.5 TB bandwidth, Full root access | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
(iii) Dedicated Server Hosting
When it comes to web hosting solutions, dedicated server hosting stands out as a powerful option for businesses and organizations that require high performance, security, and control. Let's dive into what dedicated server hosting is and how it works.
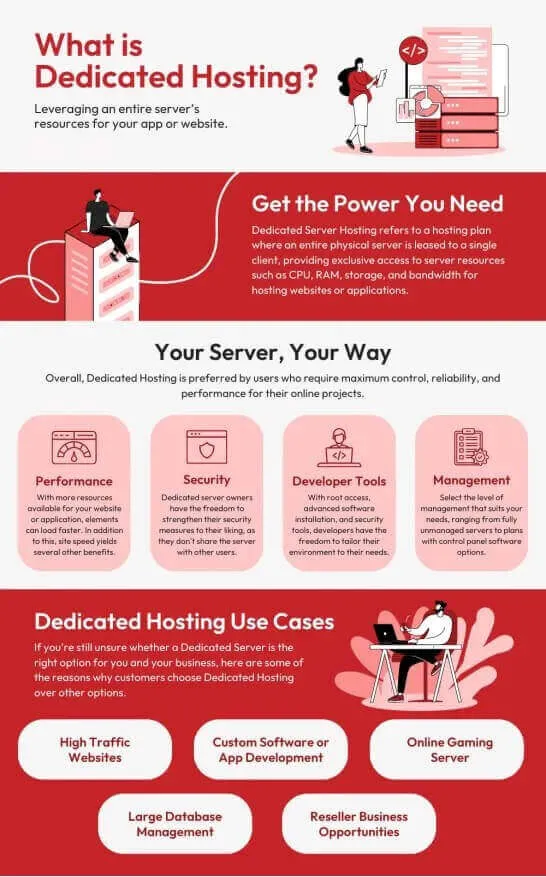
Image credit: Inmotion Hosting
What is Dedicated Server Hosting?
Dedicated Server Hosting is a type of web hosting where a physical server is exclusively allocated to a single organization or website, providing total control, security, and scalability.
Unlike shared hosting, where multiple users share the same server resources, dedicated hosting provides exclusive access to all the server's resources, including CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth. This isolation allows for enhanced performance and security, making it ideal for resource-intensive applications and very high-traffic websites.
Imagine having your own private house instead of renting a room in a shared apartment. With dedicated server hosting, you have complete control over the environment, allowing you to configure the server according to your specific needs.
Dedicated servers are particularly beneficial for large businesses, e-commerce sites, or any platform that demands high uptime and fast loading speeds. The ability to handle large amounts of data and traffic without compromising performance makes dedicated hosting a preferred choice for many organizations.
How Does Dedicated Hosting Work?
A dedicated server is housed in a state-of-the-art data center, connected to a high-performance network infrastructure and powered by redundant power lines, batteries, and generators. As the customer, you lease the server and gain access to the data center's premium resources, including lightning-fast internet bandwidth, reliable power supply, advanced air conditioning systems, and robust physical security.
You have complete authority over the server, determining who has access rights, which ports are open, what services it runs, what programming environments are allowed, and what happens when things go wrong. You're in control of custom configurations and settings, emergency protocols, and troubleshooting.
Dedicated servers are perfect for individuals and businesses with technical expertise, or those with a dedicated IT team. If you're comfortable managing and configuring servers, or have personnel to handle it for you, dedicated server hosting offers the ultimate in customization, security, and performance.
With a dedicated server, you can optimize your online presence, run resource-intensive applications, and ensure high-traffic websites load quickly and reliably.
What are the use cases of dedicated servers?
Dedicated server hosting is an excellent choice for various applications that demand high performance, security, and reliability.
Unlike shared hosting or VPS, dedicated servers provide an entire physical server solely for your use, allowing you to customize it according to your specific needs.
Let’s explore some of the most common use cases for dedicated servers.
1. High performance computing
Dedicated servers are perfect for complex computations and large data processing. They're ideal for scientific research, financial modeling, and big data analytics. For example, a weather forecasting company can use a dedicated server to process vast amounts of meteorological data to predict accurate weather patterns.
2. Data backups
Another critical use case for dedicated servers is data backups. Businesses often need robust backup solutions to protect sensitive information from loss due to hardware failures, cyberattacks, or human error.
Dedicated servers provide a secure environment for storing backups, ensuring that your data is safe and easily recoverable.
Companies often learn the importance of regular backups the hard way, such as when a server crash results in the loss of crucial files. Implementing a dedicated backup server can prevent such disasters and provide peace of mind.
Many organizations choose dedicated servers for backups because they can be configured with redundancy and high availability options to minimize downtime. For example, a financial institution can use a dedicated backup server to ensure that critical data is always available and easily recoverable in case of an emergency.
Best practices include setting up automated backup schedules and using encryption to secure your data both in transit and at rest. This way, you can ensure that your backups are not only reliable but also protected against unauthorized access.
3. Gaming
The gaming industry is another area where dedicated servers shine. Game developers often require high-performance servers to host multiplayer games that provide seamless experiences for players around the world. Dedicated servers can handle the intensive processing required for real-time interactions and large player bases without lag.
For example, a popular online multiplayer game can use a dedicated server to host games, ensuring fast loading times and a seamless gaming experience.
How does dedicated hosting differ from other hosting types?
When it comes to web hosting, understanding the differences between dedicated hosting and other types can feel overwhelming at first. But don't worry! I’ve been there, and I’m here to break it down in a way that’s easy to grasp.
Let’s dive into how dedicated hosting differs from shared hosting, VPS (Virtual Private Server), and cloud hosting.
Shared vs. dedicated hosting
When I first started my blogging journey, I opted for shared hosting because it was cheap and easy. However, as my blog grew, I quickly realized the limitations.
Shared hosting meant that my website was sharing resources with potentially hundreds of other sites. If one site on the server had a spike in traffic or got hacked, it could slow down or even crash mine!
With dedicated hosting, you get the whole server. This means faster load times and improved security because no one else’s activities can affect your site.
For example, if you’re running an e-commerce site where every second counts during checkout, dedicated hosting ensures that your site remains responsive even during peak traffic times.
VPS vs. dedicated server
Now let’s talk about VPS versus dedicated servers. When upgrading from shared hosting, a VPS (Virtual Private Server) is a significant step up, offering allocated resources like RAM and CPU power. This upgrade is similar to moving from a cramped apartment to a spacious condo, providing more room to grow.
The beauty of VPS is its scalability; you can easily upgrade your resources as needed without migrating to a new server. This flexibility is perfect for growing websites that might experience fluctuating traffic.
However, if you’re running a high-traffic site or need specific configurations (like custom software installations), dedicated hosting is the way to go. With a dedicated server, you have complete control over the hardware and software environment, which allows for optimal performance tailored to your needs.
Cloud hosting vs. dedicated hosting:
Cloud hosting is another popular option that often gets compared with dedicated servers. While both offer excellent performance and reliability, they do so in different ways.
Cloud hosting allows you to tap into multiple servers at once—like having access to an entire fleet of vehicles instead of just one car. This means if one server fails, your website can quickly switch to another without any downtime.
On the other hand, with dedicated hosting, all your resources are concentrated on one physical machine. This can lead to better performance for resource-intensive applications since there’s no competition for resources from other sites.
Here's a side-by-side comparison:
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS Hosting | Dedicated Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High | Variable (pay-as-you-go) |
| Resource Allocation | Shared among many users | Allocated resources | Entire server dedicated to you | Resources from multiple servers |
| Performance | Can be slow during peak times | Generally faster than shared | High performance | Highly reliable and scalable |
| Control | Limited control | Moderate control | Full control | Limited control over individual servers |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale | Easy to scale | Limited by hardware | Highly scalable |
| Security | Vulnerable to neighbor sites | More secure than shared | Very secure | Secure, but relies on cloud provider |
| Best For | Small personal websites | Growing websites, small businesses | High-traffic sites, e-commerce | Websites with fluctuating traffic |
| Setup Complexity | Very easy | Moderate | More complex | Moderate |
| Customization | Very limited | Some customization | Full customization | Limited customization |
What are the benefits of dedicated hosting services?
Dedicated hosting offers alot of advantages that make it a compelling choice for businesses and individuals with specific needs. Here are some key benefits:
- Dedicated Resources: Unlike shared hosting, where resources are split among multiple users, dedicated hosting provides exclusive access to all server resources. This means more CPU power, RAM, and storage, ensuring that websites run smoothly even during traffic spikes. For instance, a high-traffic eCommerce site can handle increased visitor numbers without lagging.
- Superior Performance: With dedicated hosting, the performance of your website is significantly enhanced. Since there are no other sites consuming bandwidth or processing power, load times are faster. This is crucial for user experience and can positively impact search engine rankings.
- Enhanced Security: Dedicated servers offer a higher level of security compared to shared hosting. You can implement custom security measures tailored to your needs, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. This is particularly important for businesses that handle sensitive data, like financial transactions or personal information.
- Full Customization: Dedicated hosting allows complete control over the server environment. Users can install any software or applications needed for their specific requirements, enabling a tailored hosting solution that meets unique business needs.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, their hosting needs often change. Dedicated servers can be easily scaled to accommodate increased traffic or additional applications without the need for migration to a different server.
- Reliability: With dedicated resources, uptime is significantly improved. Businesses can rely on consistent performance without the risk of being affected by "bad neighbors" on shared servers.
- Dedicated IP Address: Each dedicated server comes with its own IP address, which enhances security and can improve SEO rankings. This is particularly beneficial for eCommerce sites that require SSL certificates for secure transactions.
- 24/7 Support: Most dedicated hosting providers offer round-the-clock support to assist with any technical issues that may arise, ensuring that businesses can operate smoothly without interruptions.
Who needs a dedicated hosting server?
Dedicated hosting is ideal for several types of users and businesses:
- High-Traffic Websites: Websites that experience significant traffic spikes—like eCommerce platforms during holiday sales—benefit from the reliability and performance of dedicated servers.
- Businesses Handling Sensitive Data: Companies in finance or healthcare sectors often require enhanced security measures to protect sensitive information. Dedicated hosting provides the necessary environment to implement robust security protocols.
- Gaming Servers: Online gaming requires low latency and high performance. Dedicated servers offer the speed and stability needed for a seamless gaming experience.
- Web Applications: Businesses running resource-intensive applications benefit from dedicated resources that ensure high performance and reliability.
- Multiple Websites Management: For those managing several websites, dedicated servers provide the necessary resources and control to host multiple sites efficiently without compromising performance.
What are the disadvantages of dedicated server?
While dedicated hosting has many advantages, it’s essential to consider its drawbacks as well:
- Higher Cost: One of the most significant downsides is the cost associated with dedicated hosting. It tends to be more expensive than shared or VPS hosting options, making it less suitable for small businesses or personal websites with limited budgets.
- Requires Technical Knowledge: Managing a dedicated server often requires a higher level of technical expertise compared to other hosting types. Users need to be familiar with server management tasks such as software installation and system maintenance.
- Longer Setup Time: Setting up a dedicated server can take longer than other types of hosting due to its complexity and customization options. This might not be ideal for users looking for quick deployment.
- Resource Underutilization: If a website does not require extensive resources, investing in a dedicated server may lead to underutilization of available resources, resulting in wasted expenditure.
- Maintenance Responsibility: Although many providers offer managed services, some level of maintenance is still required from the user’s side—such as applying updates and monitoring performance—which can be time-consuming.
Common myths and misconceptions about dedicated servers
Myth 1: Dedicated Servers Are Too Expensive
One of the most prevalent myths is that dedicated hosting is prohibitively expensive. While it’s true that dedicated servers generally cost more than shared hosting, prices have significantly decreased in recent years. Many providers offer flexible pricing plans, making dedicated hosting accessible for small businesses and startups. Additionally, the long-term benefits of improved performance and security often outweigh the initial costs.
Myth 2: Only Large Businesses Need Dedicated Servers
Another common misconception is that dedicated servers are only suitable for large enterprises. In reality, businesses of all sizes can benefit from dedicated hosting. Small to medium-sized companies that require enhanced security, reliability, and performance can find dedicated solutions tailored to their needs. For example, a local online retailer experiencing rapid growth may choose a dedicated server to ensure smooth operations during peak shopping seasons.
Myth 3: Dedicated Hosting Is Complicated to Manage
Many people believe that managing a dedicated server requires extensive technical knowledge. While there is a learning curve, most hosting providers offer managed services where experts handle server maintenance and management tasks. This means users can focus on their business rather than getting bogged down by technical issues. Even unmanaged options allow for significant customization while still providing user-friendly interfaces.
Myth 4: Dedicated Servers Offer No Control
Some users worry that opting for a dedicated server means losing control over their hosting environment. This is far from the truth. Dedicated servers provide the highest level of control and customization compared to other hosting types. Users can configure their servers according to specific needs, install preferred software, and manage security settings—all while retaining administrative access.
Myth 5: Shared Hosting Is Just as Good
While shared hosting may seem appealing due to its lower cost, it often falls short in terms of performance and reliability. With shared hosting, resources are divided among multiple users, which can lead to slower load times and increased downtime during high-traffic periods. In contrast, dedicated servers provide exclusive access to resources, ensuring optimal performance even during peak usage.
Myth 6: Dedicated Servers Are Not Secure
Some believe that dedicated servers are not secure because they are hosted off-site. However, reputable hosting providers implement advanced security measures to protect data from cyber threats. This includes firewalls, DDoS protection, and regular security updates—far superior to what many individuals could achieve on their own.
Myth 7: All Dedicated Servers Are Fully Isolated
There’s a misconception that dedicated servers cannot be fully isolated from other users or systems. In reality, many providers offer fully isolated environments where resources are not shared with anyone else. This ensures maximum performance and security tailored specifically for individual needs.
How to choose a dedicated server hosting provider?
Selecting the right dedicated server hosting provider is crucial for ensuring your website's performance, security, and reliability. Here are some key factors to consider when making your choice:
- Performance and Reliability: Look for providers that guarantee high uptime percentages, ideally 99.9% or higher. This ensures your website remains accessible to users without interruptions. Check reviews and performance benchmarks to gauge reliability.
- Management Options: Determine whether you need a managed or unmanaged server. Managed services are ideal for those who prefer to focus on their business rather than server maintenance, while unmanaged options can provide more control for tech-savvy users.
- Customization and Scalability: Choose a provider that allows you to customize your server configurations, including CPU, RAM, and storage options. Scalability is also important; as your business grows, your hosting needs may change.
- Security Features: Ensure the hosting provider offers robust security measures, such as DDoS protection, firewalls, and regular backups. This is especially important for businesses handling sensitive data.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential for resolving issues quickly. Look for providers that offer 24/7 support through multiple channels like live chat, phone, and email.
- Pricing and Contract Terms: Compare pricing structures among different providers. Be cautious of hidden fees and ensure you understand the contract terms before committing. Some providers offer flexible plans that allow you to pay monthly without long-term commitments.
- Reputation and Reviews: Research the hosting provider’s reputation by reading user reviews and expert opinions. This can provide insights into their service quality and customer satisfaction.
5 Best Dedicated Server Hosting Providers
| Provider | Key Features | Price (Starting) | Management Type | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Web | High-performance servers, 99.99% uptime, excellent customer support | From $75/month | Managed | Visit Website |
| Bluehost | Budget-friendly plans, unmetered bandwidth, root access | From $79.99/month | Unmanaged | Visit Website |
| DreamHost | Flexible managed servers with a 100% uptime guarantee | From $149/month | Managed | Visit Website |
| HostGator | Fully and semi-managed options, choice of OS (Windows/Linux) | From $89.98/month | Semi or Fully Managed | Visit Website |
| InterServer | Affordable prices with customizable plans | From $70/month | Managed | Visit Website |
(iv) Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting has become a buzzword in the tech world, and for good reason. It’s a modern solution to an age-old problem: how to host applications and websites efficiently and reliably.
Let’s dive into what cloud hosting really is and how it works, drawing from my experiences and observations along the way.

What is cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting that uses a network of virtual servers, connected through the internet, to store and manage data. It's like a cloud of resources, scalable and flexible, where you can access and manage your website, applications, or data from anywhere. No more single server limitations!
At its core, cloud hosting refers to a method of hosting websites and applications using a network of virtual servers that pull their resources from extensive underlying physical servers.
Unlike traditional hosting, where your website lives on a single physical server, cloud hosting distributes your data across multiple servers.
This means that if one server goes down, your website can still run smoothly from another server in the network. It’s like having a safety net that ensures your online presence remains uninterrupted.
I remember when I first learned about cloud hosting. I was managing a small business website, and we faced frequent downtimes due to server overloads.
It was frustrating! The moment I switched to cloud hosting, everything changed. My website became more reliable, and I didn’t have to worry about traffic spikes crashing my site anymore.
The flexibility of cloud hosting allows you to scale resources up or down based on your needs, which is a game changer for businesses that experience fluctuating traffic.
How does cloud hosting work?
Understanding how cloud hosting works can be a bit tricky at first, but once you break it down, it makes perfect sense. The magic lies in virtualization technology.
Essentially, virtualization allows multiple virtual servers (or virtual machines) to run on a single physical server. Each virtual server operates independently and can draw resources as needed from the pool of available hardware.
Here’s an analogy: think of a physical server as a large pizza. Each slice represents a virtual server. When one slice (virtual server) gets busy with customers (website traffic), it can borrow ingredients (resources) from the rest of the pizza without affecting the other slices.
This means that if one virtual server experiences high traffic, it can utilize more resources without impacting others.
What are the types of cloud hosting?
When it comes to cloud hosting, understanding the different types can be a bit overwhelming at first. But once you break it down, it becomes much clearer. Each type of cloud hosting has its own unique features, benefits, and ideal use cases.
Let’s explore the four main types of cloud hosting: Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, and Managed Cloud. I’ll share insights based on my experiences and what I’ve learned along the way.
1. Public cloud
The public cloud is probably the most recognized type of cloud hosting. In this model, a third-party provider owns and manages all the hardware, software, and other infrastructure components. Users access these resources over the internet, which means you don’t have to invest in physical servers or worry about maintenance.
Popular public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure.From my personal experience, using a public cloud was a game changer for my small online store. The flexibility it offered was incredible! I could scale up my resources during peak shopping seasons without needing to buy new servers or worry about downtime.
It’s also cost-effective because you only pay for what you use. If your website traffic drops, so does your bill—no more wasting money on unused capacity.
Pro Tip: If you're just starting out or running a small business, public cloud hosting is often the best option due to its affordability and ease of use.
2. Private cloud
A private cloud is tailored specifically for one organization. This means that all the resources are dedicated solely to your business, providing enhanced security and control.
You can either manage it in-house or opt for a managed private cloud where a third-party provider handles everything for you.
For example, a government agency handling classified information can benefit from a private cloud to ensure the highest level of security and compliance. With a private cloud, they can have complete control over data storage, access, and management, minimizing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
However, managing a private cloud can be more complex and costly compared to public options.
Pro Tip:If your business handles sensitive data or requires compliance with strict regulations (like healthcare or finance), consider investing in a private cloud for better security.
3. Hybrid cloud
The hybrid cloud model combines elements of both public and private clouds. This means you can keep sensitive data on a private cloud while utilizing the public cloud for less critical operations or applications. This flexibility allows businesses to optimize their resources based on their specific needs.
For example, a financial services company can use a hybrid cloud to run their online banking platform on a public cloud, while keeping customer account information and transaction data secure on a private cloud.
This setup ensures scalability and flexibility for the online platform, while maintaining the highest security standards for sensitive customer data.
Pro Tip:If your business experiences fluctuating workloads or has varying security needs, a hybrid cloud could be the perfect solution to balance flexibility and security.
4. Managed cloud
Finally, we have the managed cloud option. In this setup, you partner with a third-party provider who manages all operational aspects of your cloud environment—everything from monitoring and security to backups and updates. This allows your team to focus on core business activities rather than getting bogged down by technical issues.
For example, an e-commerce company can benefit from a managed cloud service to ensure their online store is always available and running smoothly.
The managed cloud provider takes care of maintenance tasks such as software updates, security patches, and performance monitoring, allowing the e-commerce company to focus on product development, marketing, and customer service.
Pro Tip:If you want to leverage the power of the cloud without getting into the nitty-gritty of management, consider opting for managed cloud services.
What are the benefits of cloud hosting?
If you're considering making the switch or simply want to understand why cloud hosting is so popular, let’s break down the key benefits: Scalability, Availability, Cost Efficiency, Security, and Time to Market. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in enhancing your business operations.
1. Scalability
One of the standout features of cloud hosting is its scalability. This means you can easily increase or decrease your resources based on demand. For instance, if your website suddenly experiences a surge in traffic—say during a holiday sale—you can quickly scale up your resources to handle the load without any hassle.
2. Availability
Availability is another major benefit of cloud hosting. With traditional hosting solutions, if one server goes down, your entire website could be offline until the issue is resolved.
On the other hand, cloud hosting operates on a network of servers, meaning that if one server fails, others can take over seamlessly.This redundancy is crucial for businesses that rely on their online presence.
3. Cost efficiency
Cloud hosting is often more cost-efficient than traditional hosting solutions. With cloud services, you only pay for the resources you use. This means no more paying for excess capacity that sits idle most of the time.
You can scale resources up or down depending on your needs, which helps manage operational costs effectively.
For example, during quieter months for my e-commerce site, I could reduce my server capacity and cut costs without sacrificing performance during peak times. This flexibility has allowed me to allocate budget more effectively across other areas of my business.
4. Security
Security is the very essential thing for businesess. Cloud hosting providers typically invest heavily in security measures like data encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits. The distributed nature of cloud environments also adds an extra layer of protection; if one server is compromised, it doesn’t necessarily affect others.
I’ve learned that while no system is completely immune to attacks, the advanced security protocols used by reputable cloud providers significantly reduce risks. Additionally, many offer features like automatic backups and disaster recovery options, which are invaluable for business continuity.
5. Time to market
Finally, cloud hosting can drastically reduce your time to market for new products or services. With traditional setups, provisioning new servers or infrastructure can take weeks or even months. However, with cloud hosting, you can deploy new applications or services almost instantly.
For instance, a software company can quickly launch a new version of their product to respond to customer feedback or changing market conditions.
With cloud hosting, they can spin up new servers and deploy the updated software in a matter of hours, rather than weeks or months.
This rapid deployment capability enables businesses to stay agile and competitive in today's fast-paced market.
What are the disadvantages of Cloud Hosting?
While cloud hosting offers numerous advantages, it is essential to be aware of its potential disadvantages. Understanding these drawbacks can help businesses make informed decisions about their cloud strategies. Let's explore the key disadvantages of cloud hosting:
1. Dependency on Internet Connectivity
Cloud hosting relies heavily on a stable internet connection. If your internet connection is unstable or experiences outages, your cloud-hosted services will be inaccessible. Additionally, slow internet speeds can impact the performance of your applications and websites.
2. Security Concerns
While cloud providers implement robust security measures, there's always a risk of data breaches. Additionally, you have less control over your data security compared to on-premises solutions, as you are relying on the cloud provider's security infrastructure.
3. Vendor Lock-in
Once you've invested in a cloud provider's infrastructure, it can be difficult to switch to another due to proprietary technologies and data migration challenges. This can limit your flexibility and potentially lead to higher costs over time.
4. Performance Limitations
Depending on the geographic location of the data center and your users, there may be latency issues, affecting application responsiveness. Additionally, high network traffic can impact performance, especially during peak usage times.
5. Cost Considerations
While cloud hosting can be cost-effective in the short term, unexpected costs like data transfer fees, storage costs, and additional services can accumulate over time. Additionally, long-term contracts with cloud providers may limit your flexibility and increase costs.
6. Limited Control Over Hardware and Software
Cloud hosting provides less control over the underlying hardware and software infrastructure compared to on-premises solutions. This means you're reliant on the cloud provider to keep the infrastructure updated and secure.
What is the difference between web hosting and cloud hosting?
In this section, we will explore the distinctions between VPS hosting, Dedicated Hosting, and Shared Hosting compared to cloud hosting.
1. VPS hosting vs. cloud hosting
VPS (Virtual Private Server) Hosting provides users with a dedicated portion of a physical server, offering more control and resources than shared hosting. However, it remains limited by the physical server's capacity. In contrast, cloud hosting utilizes a network of multiple servers, enabling it to distribute resources efficiently across various machines.
Key Differences:
- Scalability: Cloud hosting is highly scalable, allowing for on-demand resource allocation to handle traffic spikes. VPS hosting can also be scaled but requires manual adjustments and is limited by the physical server's capabilities.
- Performance: Cloud hosting often delivers superior performance due to its ability to draw from multiple servers, while VPS performance can suffer if the host server experiences high demand.
- Control: VPS hosting provides users with root access and greater customization options, whereas cloud hosting typically offers a more managed environment with limited user control.
2. Dedicated hosting vs. cloud hosting
Dedicated Hosting involves renting an entire physical server exclusively for your website or application. This setup offers maximum performance and control but comes with higher costs and maintenance responsibilities. On the other hand, cloud hosting distributes resources across multiple servers, providing flexibility and scalability without the need for dedicated hardware.
Key Differences:
- Resource Allocation: Dedicated hosting provides fixed resources that are not shared with others, while cloud hosting allows for dynamic resource allocation based on current needs.
- Cost Structure: Dedicated hosting usually involves a fixed monthly fee regardless of usage, whereas cloud hosting often operates on a pay-as-you-go model, making it potentially more cost-effective for fluctuating workloads.
- Maintenance: With dedicated hosting, users are responsible for server maintenance and updates. In contrast, cloud providers typically manage these aspects, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations.
3. Shared hosting vs. cloud hosting
Shared Hosting is the most basic form of web hosting where multiple websites share a single server's resources. This option is cost-effective but comes with limitations in performance and control. In comparison, cloud hosting offers enhanced performance, scalability, and reliability by utilizing multiple servers.
Key Differences:
- Performance: Shared hosting can lead to slow loading times during peak traffic periods as resources are divided among many users. Cloud hosting mitigates this issue by distributing traffic across multiple servers.
- Security: Shared hosting environments can be less secure due to the shared nature of resources; if one site is compromised, others may be at risk. Cloud hosting generally provides better security measures due to its distributed architecture.
- Cost Efficiency: While shared hosting is typically cheaper than both VPS and dedicated options, cloud hosting can be more cost-effective in the long run due to its scalability and resource efficiency.
Here's a side-by-side comparison:
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS Hosting | Dedicated Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High | Variable |
| Performance | Limited | Good | Excellent | High |
| Resource Allocation | Shared | Dedicated Virtual | Full Control | Dynamic |
| Security | Basic | Good | Excellent | High |
| Scalability | Limited | Moderate | Low | High |
| Maintenance | Provider Managed | User Managed | User Managed | Provider Managed |
How to choose a cloud hosting provider?
Choosing the right cloud hosting provider is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business operations and data security. With so many options available, it’s essential to evaluate potential providers thoroughly. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to choose a cloud hosting provider:
1. Compliance with Industry Standards
One of the first steps in selecting a cloud hosting provider is to ensure they comply with relevant industry standards. Compliance frameworks like ISO 27001, GDPR, and PCI DSS are crucial for maintaining data security and privacy.
These standards help ensure that the provider has implemented necessary security controls and practices.
2. Evaluating Operational Workflows
Understanding the operational workflows of a cloud provider is vital for ensuring that their processes align with your business needs. This includes evaluating how they handle data storage, processing, and backup. A well-defined workflow can enhance efficiency and minimize risks associated with data management.
Look for providers that offer clear documentation of their operational processes, including how they manage data access and monitoring. This transparency can help you gauge their reliability and responsiveness to potential issues.
3. Evaluate Authentication Methods
Strong authentication methods are essential for protecting sensitive data in the cloud. When choosing a provider, assess their authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO). These methods add layers of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple means.
Additionally, inquire about how the provider manages user permissions and access controls. Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information is crucial for maintaining data integrity.
4. Evaluating Vendor’s Access and Control
It’s important to evaluate how much access and control you will have over your cloud environment. Some providers may offer limited control over configurations or resource management, which could hinder your ability to customize your setup according to your needs.
Ensure that the provider allows you sufficient control over your resources while also maintaining necessary security measures. This balance is essential for optimizing performance without compromising security
5. Evaluate Corporate Audit Logs
Corporate audit logs provide valuable insights into user activities and system changes within the cloud environment. When selecting a provider, inquire about their logging practices and whether they maintain comprehensive audit trails.
These logs are crucial for identifying potential security incidents or compliance violations. A good cloud provider should offer tools for monitoring logs regularly and generating reports for audits.
6. Evaluate Internal Resources
Assessing the internal resources of a cloud hosting provider is vital for understanding their capabilities and support structures. This includes evaluating their technical expertise, customer support availability, and infrastructure resilience.
A provider with strong internal resources can offer better support during implementation and ongoing operations. Look for providers that have dedicated teams for customer service and technical assistance.
7. Review the SLA
The Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a critical document that outlines the terms of service between you and the cloud provider. It typically includes performance metrics, uptime guarantees, response times for support requests, and penalties for non-compliance.
Reviewing the SLA carefully ensures that it aligns with your business expectations and compliance requirements. Pay attention to any clauses related to data ownership, service continuity, and termination policies.
8. Evaluate 3rd-party Integrations
Assessing the ability of a cloud provider to integrate with third-party applications is essential for ensuring compatibility with your existing systems. Many businesses rely on various software tools for operations; thus, seamless integration can enhance productivity and reduce operational friction.
Check if the provider supports popular integrations or offers APIs that allow customization based on your specific needs.
9. Evaluate Reliability & Performance Health
The reliability and performance health of a cloud hosting provider are crucial factors in ensuring consistent service delivery. Look for providers that offer uptime guarantees (ideally above 99.9%) and have mechanisms in place for monitoring performance metrics.
Evaluate their historical performance records through customer reviews or independent assessments to gauge reliability over time.
10. Track the History of Data Breaches & Network Intrusions
Researching the history of data breaches or network intrusions associated with potential providers is essential for assessing risk levels. Providers should have transparent policies regarding past incidents and demonstrate how they addressed vulnerabilities to prevent future occurrences.
Understanding their incident response strategies can provide insights into their commitment to security.
11. Evaluate Disaster Recovery Plan
A robust disaster recovery plan is vital for minimizing downtime in case of unexpected events such as natural disasters or cyberattacks. When selecting a cloud provider, inquire about their disaster recovery strategies, including backup protocols, failover procedures, and recovery time objectives (RTO).
Ensure that their plan aligns with your business continuity requirements to mitigate risks effectively.
12. Services & Support During Transition
Transitioning to a new cloud environment can be complex; therefore, evaluating the level of services and support during transition is crucial. Look for providers that offer comprehensive onboarding assistance, training resources, and migration support to facilitate a smooth transition process.
A supportive transition team can significantly reduce disruptions during migration while ensuring that your team is well-equipped to manage the new environment effectively.
13. Review Termination Policies
Finally, reviewing the termination policies of potential cloud providers is essential before making a commitment. Understand what happens to your data if you decide to terminate services—whether it will be deleted securely or if there are any retention policies in place.
Clear termination policies can help prevent potential legal issues or data loss when transitioning away from a service provider.
5 Best Cloud Hosting Providers
| No. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Varies | Scalable, pay-as-you-go, wide range of services | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Varies | AI and machine learning, scalable, global network | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | Microsoft Azure | Varies | Integrated with Microsoft products, scalable, enterprise-grade security | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | DigitalOcean | From $5/mo | Simple, developer-friendly, scalable | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | Linode | From $5/mo | Affordable, high-performance, developer-friendly | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
(v) Managed Hosting

What is managed hosting?
Managed hosting is a type of web hosting where the provider manages and maintains the servers, operating system, and applications for you. This includes security updates, backups, monitoring, and technical support.
Customers typically have administrative access but often choose to interact with their systems through a user-friendly web interface rather than managing the technical details themselves.
Managed vs Unmanaged Hosting
When comparing managed hosting to unmanaged hosting, the primary distinction lies in the level of control and responsibility assigned to the customer.
Managed Hosting
- Responsibility: The provider handles all technical management tasks, including server maintenance, updates, security measures, and troubleshooting.
- Support: Customers benefit from round-the-clock technical support, allowing them to focus on their business rather than IT issues.
- Customization: Managed hosting can be tailored to meet specific business needs, offering flexibility in resource allocation and service options.
- Cost Efficiency: While managed hosting may have higher upfront costs compared to unmanaged options, it can save businesses money in the long run by reducing the need for in-house IT staff and minimizing downtime.
Unmanaged Hosting
- Responsibility: Customers are responsible for managing every aspect of their server environment, including software installation, updates, security configurations, and troubleshooting.
- Support: Limited or no technical support is provided; users must rely on their own expertise or external resources for assistance.
- Control: Offers greater control over server settings and configurations but requires a higher level of technical knowledge.
- Cost Considerations: Unmanaged hosting solutions are often cheaper initially but can lead to higher costs due to potential downtime or security breaches if not managed properly.
Here's a side-by-side comparison:
| Feature | Managed Hosting | Unmanaged Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Responsibility | Provider manages all server-related tasks | Customer manages all aspects of server |
| Technical Support | 24/7 support available | Limited or no support |
| Customization | Tailored services based on business needs | Full control over configurations |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher costs but potential long-term savings | Lower initial costs but possible hidden costs |
| Expertise Required | Minimal technical knowledge needed | Requires significant technical expertise |
| Security Management | Comprehensive security measures included | Customer responsible for security |
| Backup Solutions | Regular automated backups provided | Customer must implement their own backup plan |
Benefits of Managed Hosting
Understanding the benefits and disadvantages of both managed hosting and unmanaged hosting is essential for making informed decisions. Each type has its unique features, advantages, and drawbacks that cater to different business needs. Let’s explore these aspects in detail.
- Expert Support and Management: Managed hosting provides round-the-clock support from a team of experts who handle all technical aspects. This means that businesses can focus on their core activities without worrying about server management, updates, or security issues.
- Enhanced Security: Managed hosting services typically include robust security measures such as firewalls, malware detection, and regular security audits. Providers actively monitor for threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring that your data remains secure.
- Automatic Backups: With managed hosting, automated backups are standard practice. This feature ensures that your data is regularly backed up without manual intervention, providing peace of mind in case of data loss or server failure.
- Performance Optimization: Managed hosting providers often optimize server settings for better performance. They can fine-tune configurations to enhance loading speeds and overall site performance, which is crucial for user experience and SEO.
- Scalability: Managed hosting solutions are typically designed to scale easily with your business needs. As traffic increases or your resource requirements change, providers can adjust resources without significant downtime or complications.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many managed hosting providers adhere to industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA. This compliance is vital for businesses handling sensitive data, ensuring that they meet legal requirements.
Disadvantages of Managed Hosting
- Higher Costs: One of the primary drawbacks of managed hosting is the cost. While it provides numerous benefits, the price can be significantly higher than unmanaged options, which may not be feasible for small businesses or startups.
- Limited Control: Users may have less control over their server configurations compared to unmanaged hosting. This limitation can be a drawback for businesses that require specific customizations or have unique technical needs.
- Dependency on Provider: Relying on a third-party provider for server management means that any issues on their end could impact your operations. If the provider experiences downtime or service disruptions, your business may suffer as well.
- Potential for Overhead: Some managed services may include features that your business does not need, leading to unnecessary costs. It's important to carefully evaluate what services are included in the package.
Benefits of Unmanaged Hosting
- Cost-Effectiveness: Unmanaged hosting is generally less expensive than managed options. This affordability makes it an attractive choice for startups or small businesses with limited budgets.
- Full Control: Users have complete control over their server environment with unmanaged hosting. This freedom allows for extensive customization and flexibility in configuring the server according to specific needs.
- Root Access: With unmanaged hosting, users typically receive root access to their servers, enabling them to install any software or applications they require without restrictions.
- Learning Opportunity: Managing your own server can provide valuable experience and knowledge about server administration and web technologies, which can be beneficial for tech-savvy individuals or teams
Disadvantages of Unmanaged Hosting
- Technical Expertise Required: Unmanaged hosting requires a higher level of technical knowledge and expertise. Businesses without a dedicated IT team may struggle with server management tasks such as updates, security configurations, and troubleshooting.
- No Support: Unlike managed hosting, unmanaged services offer little to no technical support. Users must rely on their own skills or seek external help when issues arise, which can lead to downtime and potential losses.
- Increased Security Risks: Without professional management, unmanaged servers may be more vulnerable to security breaches and attacks. Users must implement their own security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Time-Consuming Maintenance: Managing an unmanaged server requires significant time investment for maintenance tasks such as backups, updates, and monitoring performance metrics.
- Potential Downtime Costs: If issues arise due to mismanagement or lack of expertise, businesses may face significant downtime costs that could impact revenue and customer satisfaction.
Who Should Use Managed Hosting?
Small Business Owners: If you run a small business and don’t have an IT team, managed hosting can be a lifesaver. I remember when I first started my online store. I was overwhelmed with the technical aspects of running a website. From security updates to server maintenance, it felt like I was juggling too many balls at once. Switching to managed hosting meant I could spend more time focusing on my products and less time worrying about whether my website was secure or running smoothly.
E-commerce Sites: If you’re running an e-commerce site, uptime and performance are crucial. Customers expect a seamless shopping experience, and any downtime can lead to lost sales. A managed hosting provider ensures that your site is always up and running, with 24/7 monitoring and support. I once had a friend whose online shop crashed during a big sale because he was on shared hosting. He lost thousands in revenue because he couldn’t get help in time. With managed hosting, those kinds of disasters can be avoided.
Content Creators and Bloggers: For bloggers or content creators who want to focus on writing rather than managing servers, managed hosting is ideal. It allows you to concentrate on creating engaging content while the hosting provider takes care of the technical details. I’ve seen many bloggers struggle with server issues that distract them from their writing. With managed hosting, you can rest easy knowing that your site is in good hands.
Developers and Agencies: If you’re a developer or part of an agency working with multiple clients, managed hosting can streamline your workflow. You won’t have to worry about server management for each project; instead, you can focus on building great applications or websites.
How to choose a managed hosting provider?
Now that we’ve established who should consider managed hosting, let’s talk about how to choose the right provider. There are several factors to consider:
1. Cost and pricing transparency
First off, look at the cost. Managed hosting can be more expensive than shared hosting, but it’s essential to find a provider that offers transparent pricing without hidden fees.
Imagine you're planning to launch an e-commerce website with fluctuating traffic. You need a hosting provider that offers flexible pricing plans. Look for providers with transparent pricing models, no hidden fees, and scalable plans that adapt to your changing needs.
2. Type of website or application
Consider the type of website or application you’re running. Some providers specialize in specific platforms like WordPress or e-commerce solutions. For example, if you’re using WordPress, look for a host that offers optimized WordPress plans with built-in caching and security features.
3. Support tiers
Support is another critical factor. Different providers offer varying levels of support—some provide basic assistance while others offer 24/7 premium support.
Let's suppose your website experiences sudden downtime during peak hours. You need immediate assistance from your hosting provider. Opt for providers offering multi-channel support (phone, email, chat), guaranteed response times, and dedicated account managers for critical issues.
4. Security services
Security should never be an afterthought. Ensure your chosen provider has robust security measures in place—this includes firewalls, malware scanning, and regular updates. Cybersecurity risks are real; I've heard stories from colleagues who faced significant data breaches due to inadequate security measures from their hosts.
5. Performance and scalability
Lastly, consider performance and scalability options. As your website grows, you’ll want a host that can accommodate increased traffic without sacrificing speed or performance. Look for features like Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and SSD storage for faster load times.
Pro Tip: Before fully committing to a managed hosting provider, take advantage of free trials or money-back guarantees if they offer them. This way, you can test their services without any long-term commitment.
5 Best Managed Hosting Services Provider
| NO. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bluehost | From $19.95/mo | Free Domain, SSL, 24/7 Support, Enhanced cPanel | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | Hostinger | From $9.99/mo | Free Domain, SSL, 24/7 Support, Daily Backups | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | InterServer | From $6.00/mo | Unlimited Storage, 24/7 Support, Free Migration | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | Namecheap | From $1.58/mo | Free Domain, 24/7 Support, Free CDN | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | Cloudways | From $10.00/mo | Free SSL, 24/7 Support, Managed Backups | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
(vi) Reseller Hosting
Reseller hosting is an exciting and accessible way to dive into the world of web hosting without the hefty price tag that usually comes with it. If you’ve ever thought about starting your own hosting business but felt overwhelmed by the technical side of things or the costs involved, reseller hosting might just be your golden ticket.
Let’s break down what reseller hosting is, the role of reseller hosting providers, and the key features and benefits that make this option so appealing.
Image credit: Inmotion Hosting
What is Reseller Hosting?
Reseller hosting is a type of web hosting where you purchase hosting services in bulk from a provider and resell them to your own clients.
You essentially become a middleman, offering hosting services under your own brand, while the original provider manages the infrastructure and technical aspects.
This means you can offer various hosting plans tailored to different needs without having to invest in expensive infrastructure or server maintenance.
Instead of worrying about hardware, you can focus on building your brand and customer relationships.
Think of it like buying a bulk pack of snacks and then selling them individually at a markup. You don’t need to create the snacks yourself; you simply buy them at a wholesale price and sell them to your friends or customers.
The Role of Reseller Hosting Providers
Reseller hosting providers play a crucial role in this arrangement. They handle all the technical aspects, such as server maintenance, security updates, and customer support. This means that as a reseller, you can focus on marketing your services and managing your clients without getting bogged down by the nitty-gritty details of server management.
For instance, many providers offer white-label solutions, which allow you to brand the services as your own. Your clients won’t even know they’re using a service that comes from another company; they’ll see your logo and branding everywhere. This helps build trust and credibility with your customers.
Key Features and Benefits
Now that we’ve established what reseller hosting is and who the providers are, let’s dive into some key features and benefits that make this option so attractive for aspiring entrepreneurs.
Affordability
One of the biggest advantages of reseller hosting is affordability. Starting a traditional web hosting business can be prohibitively expensive. You’d need to invest in servers, data centers, and technical staff.
With reseller hosting, those costs are significantly reduced because you’re leveraging existing infrastructure from a larger provider. You can start small with minimal upfront investment and scale up as your business grows.
Manageability
Managing multiple clients can be daunting, but reseller hosting makes it easier. Each client gets their own account with unique login credentials, allowing them to manage their websites independently.
You can administer these accounts without needing constant access to their login information. This streamlined management process saves time and reduces headaches.
Scalability
As your business grows, so do your needs. Reseller hosting plans are designed to be scalable. You can start with a smaller package that fits your current customer base and upgrade as needed when demand increases. This flexibility ensures that you’re not paying for more than you need upfront.
No Technical Expertise Required
You don’t need to be a tech whiz to start a reseller hosting business. Most reputable providers offer comprehensive support services, including technical assistance, automated backups, and security features. This means you can focus on customer service rather than troubleshooting server issues.
Brand Building
With white-label options available through many reseller hosts, you have the opportunity to build your own brand from day one. You can create a unique identity for your business that resonates with your target audience without worrying about the underlying technology.
Access to Additional Features
Many reseller hosting plans come with valuable features like free SSL certificates, control panels (like cPanel or Plesk), unlimited bandwidth options, and one-click app installers for easy software management. These features not only enhance the service you provide but also make it easier for clients to manage their websites.
Recurring Revenue Potential
By offering web hosting services through reseller plans, you create an opportunity for recurring revenue streams. Customers typically pay monthly or annually for their hosting services, meaning once you've built up a client base, you could enjoy consistent income with relatively low ongoing effort.
How Does Reseller Hosting Work?
Reseller hosting operates on a straightforward model. Essentially, you purchase a bulk hosting package from a larger hosting provider, which includes server resources like storage space, bandwidth, and sometimes even additional features such as SSL certificates and automated backups. This package is then divided into smaller hosting plans that you can sell to your own customers under your brand name.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
- Choose a Hosting Provider: The first step is selecting a reliable hosting provider that offers reseller plans. Look for one that provides good support, scalability options, and features that align with your business goals.
- Set Up Your Reseller Account: After signing up, you’ll create a reseller account. This account gives you access to wholesale pricing and allows you to manage your clients' accounts.
- Customize Your Packages: You’ll have the flexibility to create different hosting packages based on the resources you’ve purchased. This could mean offering various tiers of service with different levels of storage, bandwidth, and features.
- Branding: One of the best parts about reseller hosting is that you can brand these packages as your own. You can customize the control panel with your logo and company name, making it look professional and trustworthy to your clients.
- Market and Sell: Once everything is set up, it’s time to start marketing your services! You can sell these plans at a markup, allowing you to earn profits from each sale.
How to Start Reselling Web Hosting Services
Starting a reseller hosting business can be an exciting venture, especially if you’re looking to provide web hosting services without the heavy lifting of managing servers and technical infrastructure.
If you’re ready to take the plunge into this world, here’s a step-by-step guide on how to start reselling web hosting services, including key considerations and tips along the way.
1. Create a Business Plan
Before diving into any business, it’s essential to outline a clear business plan. Think of this as your roadmap. What are your goals? Who are your target customers? What services will you offer? A solid plan should include your business model, marketing strategies, and financial projections. This doesn’t need to be overly complicated; even a simple outline can help you stay focused and organized.
I remember when My Friend first started; He didn’t take the time to plan properly. He jumped right in and ended up overwhelmed with decisions later on. Having a plan would have saved me a lot of headaches!
2. Choose a Reseller Hosting Plan
Next, you’ll need to research and select a reseller hosting plan that fits your needs. Look for providers that offer robust features like white-label branding, good customer support, and scalability options. You want a plan that allows you to grow as your customer base expands.
3. Set Your Prices and Packages
Once you’ve chosen a reseller hosting plan, it’s time to set your prices. Consider the wholesale price you’re paying and how much you want to mark up your services. It’s important to strike a balance between being competitive in the market while also ensuring you make a profit.
Think about creating tiered packages—like basic, standard, and premium—so customers can choose what best fits their needs. For instance, if you're offering more resources or features in higher tiers, make sure the price reflects that value
4. Branding and Customization
Branding is crucial in establishing your presence in the market. Customize your hosting packages with your logo and unique branding elements. This not only helps build trust but also makes your service feel more professional.
Take some time to create an appealing website where potential clients can learn about your services. When you first start branding your services then don't underestimate how much of an impact it will have on your credibility with clients.
5. Set Up a Website and Online Presence
Your website will be the face of your business, so invest time in creating an attractive and user-friendly site. Make sure it clearly outlines your offerings, pricing plans, and contact information.
Additionally, consider setting up social media profiles to engage with potential customers and promote your services. Content marketing—like blogging or posting helpful articles—can also attract traffic to your site.
6. Market Your Reseller Hosting Business
Now that everything is set up, it’s time to spread the word! Use various marketing strategies such as SEO (search engine optimization), social media marketing, and even paid advertising if your budget allows.
Networking with local businesses or online communities can also help you gain visibility. My Friend found that joining forums related to web development helped me connect with potential clients who were looking for hosting solutions.
7. Provide Customer Support
Excellent customer support is key in retaining clients and building a good reputation. Since you’re reselling services from another provider, ensure you understand their support systems so you can assist customers effectively.
Consider offering multiple channels for support—like email, chat, or phone—to make it easy for clients to reach out when they need help.
8. Billing and Payment Processing
Setting up billing and payment processing is vital for managing client accounts efficiently. Many reseller hosting providers offer integrated billing solutions like WHMCS or Blesta that automate invoicing and payment reminders.This not only saves you time but also helps keep everything organized as your client base grows
9. Launch and Onboard Clients
Once everything is in place, it’s time for the big launch! Start onboarding clients by guiding them through the setup process smoothly.
Provide them with all necessary information about their accounts and how they can manage their hosting services. Creating welcome emails or guides can enhance their experience right from the start.
10. Monitor and Maintain Server Performance
As a reseller, while you don’t manage the servers directly, it’s still important to monitor performance metrics like uptime and response times regularly. Keeping an eye on these factors ensures that your clients have a positive experience with their hosting service.
If issues arise with server performance from the main provider's end, be proactive in communicating with your clients about resolutions.
11. Continue to Improve and Expand
Finally, always look for ways to improve your offerings and expand your business. Gather feedback from clients about what they like or what could be better; this information is invaluable for growth.
Consider diversifying into additional services like domain registration or website development as you become more established in the market.
You can create additional Revenue Streams
Reseller hosting not only allows you to sell web hosting services but also opens doors to various additional revenue streams. Here are some ideas:
1. Domain Registration Services
Many reseller hosting providers offer domain registration services as part of their packages. By adding domain registration to your offerings, you can provide a complete solution for clients looking to establish their online presence. You can charge a fee for each domain registered, creating another income source.
2. Website Development Services
If you have skills in web design or development, consider offering these services alongside your hosting packages. Many businesses need help building their websites or maintaining them after launch. By providing website development services, you can charge clients for both hosting and design work.
3. Managed Services
You can offer managed services as an upsell to your basic hosting plans. This could include regular backups, security monitoring, software updates, or even content management services for clients who prefer a hands-off approach. Clients are often willing to pay extra for peace of mind knowing their website is being taken care of by professionals.
4. Email Hosting
Another potential revenue stream is email hosting services. Many businesses require professional email addresses linked to their domain names (like [email protected]). By offering email hosting as an add-on service, you can provide additional value while increasing your earnings.
5. Affiliate Marketing
If you're not ready to dive into selling directly or want to supplement your income further, consider affiliate marketing with other web-related services like SEO tools or online marketing platforms. By promoting these products through your website or blog, you can earn commissions on any sales generated through your referral links.
6. Online Courses or E-books
If you've gained expertise in web hosting or related fields over time, consider creating online courses or e-books that teach others how to navigate this space effectively. You could charge for access to these resources while positioning yourself as an authority in the industry.
Finding the Best Reseller Hosting Provider
When selecting a reseller hosting provider, it’s essential to consider several factors that can significantly impact your business. Here are some key elements to look for:
1. Reliability and Uptime
Choose a provider that guarantees high uptime—ideally 99.9% or higher. This ensures your clients’ websites remain accessible, which is critical for customer satisfaction.
2. Support Services
Look for providers that offer 24/7 customer support. As a reseller, you’ll need to rely on your host’s support team to assist with technical issues that your clients may encounter.
3. White-Label Solutions
A good reseller hosting provider should offer white-label solutions, allowing you to brand their services as your own. This helps build trust with your clients since they’ll see your branding rather than that of the hosting company.
4. Features and Tools
Consider what features are included in the plans—such as cPanel/WHM access, free SSL certificates, automated backups, and billing software like WHMCS. These tools can simplify management and enhance your service offerings.
5. Pricing
Compare pricing across different providers to ensure you’re getting value for your money. Some popular options include A2 Hosting, InMotion Hosting, SiteGround, HostGator, and Liquid Web. Each has its strengths in terms of performance and customer support.
Pricing and Packaging Your Plans
Once you’ve chosen a hosting provider, it’s time to decide how you’ll price and package your services. Here are some steps to guide you:
1. Understand Your Costs
Calculate the wholesale cost of your reseller plan and determine how much you want to mark up your prices. Consider factors like server resources, support costs, and any additional services you plan to offer.
2. Create Tiered Packages
Offer multiple packages at different price points to cater to various customer needs. For example:
- Basic Plan: Limited storage and bandwidth for small websites.
- Standard Plan: More resources suitable for growing businesses.
- Premium Plan: Unlimited storage and bandwidth for larger enterprises.
This tiered approach allows clients to choose a plan that fits their requirements while providing opportunities for upselling.
3. Monitor Competitor Pricing
Keep an eye on what competitors are charging for similar services. This will help you stay competitive while ensuring that your offerings remain attractive to potential customers.
Marketing Strategies
Effective marketing is key to attracting clients to your reseller hosting business. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Content Marketing
Start a blog or create informative content related to web hosting, website design, or online business tips. This not only positions you as an authority in the field but also helps with SEO (search engine optimization) to attract organic traffic.
2. Social Media Engagement
Utilize social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn to promote your services. Share valuable content, engage with followers, and run targeted ads to reach potential customers.
3. Networking
Join online forums or local business groups where potential clients might gather. Networking can lead to referrals and partnerships that can boost your visibility.
4. Offer Promotions
Consider running promotional campaigns or discounts for new customers or during special events (like Black Friday). This can encourage sign-ups and help build initial momentum for your business.
Challenges of Reseller Hosting
While reseller hosting offers many benefits, there are challenges you may encounter:
1. Technical Issues
Even though the primary host handles server management, technical issues can still arise that affect your clients’ websites. You need to be prepared to address these problems quickly or communicate effectively with your host's support team.
2. Competition
The web hosting market is saturated with providers offering similar services at competitive prices. Standing out requires effective marketing strategies and exceptional customer service.
3. Customer Retention
Keeping clients satisfied is crucial for long-term success. If customers experience downtime or poor support from the main hosting provider, it reflects poorly on you as their reseller.
5 Best Reseller Hosting Providers
| NO. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Verpex | From $9.99/mo | Free SSL, Daily Backups, 24/7 Support | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | HostGator | From $19.95/mo | Free SSL, WHM Control Panel, 24/7 Support | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | InterServer | From $19.95/mo | Unlimited Storage, Free Migration, 24/7 Support | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | Namecheap | From $19.88/mo | Free Domain, Free CDN, 24/7 Support | 4.3/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | A2 Hosting | From $13.19/mo | Free SSL, WHM Control Panel, 24/7 Support | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
(vii) WordPress Hosting

What is WordPress Hosting?
WordPress hosting is a specialized service that provides the resources and infrastructure needed to run a WordPress website. Unlike standard web hosting, which can cater to any type of website, WordPress hosting is tailored specifically for WordPress sites.
This means it often includes features that enhance performance, security, and ease of use for WordPress users. I remember when I first started my blog. I was overwhelmed by the choices available.
I ended up picking a host that seemed affordable but didn’t offer any of the features specific to WordPress. It was a learning experience! My site was slow, and I struggled with updates and security issues until I switched to a host designed for WordPress.
Types of WordPress Hosting
There are several types of WordPress hosting options available, each catering to different needs and budgets:
1. Shared WordPress Hosting
Shared WordPress Hosting is often the most affordable option for beginners. With this type of hosting, multiple websites share the same server resources. While it’s budget-friendly, it can lead to slower performance if other sites on the server experience high traffic.
2. WordPress VPS Hosting
VPS (Virtual Private Server) WordPress Hosting strikes a balance between shared and dedicated hosting. With VPS hosting, you still share a server but have dedicated resources allocated just for your site.
This option offers better performance and scalability without the higher costs associated with dedicated servers.
3. Dedicated WordPress Hosting
If you’re running a high-traffic site or an e-commerce store, Dedicated WordPress Hosting might be worth considering. With dedicated hosting, you have an entire server dedicated solely to your website. This means you get maximum performance and control over your environment.
I once worked with a client who had a rapidly growing online store. We moved them to dedicated hosting to handle their traffic spikes during sales events. The difference was night and day—faster load times and improved user experience led to increased sales.
4. Managed WordPress Hosting
Managed WordPress Hosting takes care of all the technical aspects for you. This means your provider will handle updates, backups, security monitoring, and more. It’s perfect for those who want to focus on creating content rather than managing their site’s backend.
When I switched to managed hosting, it felt like a weight had been lifted off my shoulders. My provider took care of everything from daily backups to security checks.
Plus, many managed hosts offer performance optimizations that can significantly improve your site speed—something that Google loves for SEO!
What is Included in WordPress Hosting?
Let’s explore what you can expect from a quality WordPress hosting service, breaking it down into bite-sized pieces.
1. WordPress Pre-Installed
One of the most convenient features of WordPress hosting is that it often comes with WordPress pre-installed. This means you can skip the technical hassle of setting up the software yourself.
For example, a small business owner can quickly launch their website without worrying about technicalities, focusing on creating content and growing their online presence.
2. Free Domain
Many hosting providers include a free domain registration with their plans. This is an excellent perk because it means you don’t have to go through the hassle of registering your domain separately.
3. Free SSL Certificate
Security is paramount, especially if you’re handling sensitive information on your site. A free SSL certificate ensures that data transferred between your website and your visitors is encrypted, which is crucial for building trust.
4. Automatic WordPress Updates
As your WordPress site matures, managing updates becomes an ongoing challenge. Automated updates simplify the process, but it's equally crucial to have a reliable rollback option. This safety net allows you to revert to a previous version if an update causes compatibility issues with your theme or plugins.
Having a rollback option provides peace of mind, ensuring that you can quickly recover and adapt to any unexpected changes. You can address theme or plugin requirements affected by the update and find alternative solutions for critical site functions impacted by the update.
This keeps your site running smoothly and minimizes downtime. With the ability to rollback updates, you can breathe easier knowing that you have a backup plan in place to ensure your site's stability and performance.
5. Automatic Backups and Site Restoration
Imagine waking up one day to find your website has crashed or been hacked! With automatic backups, you can rest easy knowing that your site’s data is regularly backed up and can be restored easily if something goes wrong.
When I experienced my one blog site crash due to a plugin conflict, having backups saved me from losing weeks of work.
6. Free Website Migration
If you’re moving from another host, many quality WordPress hosting services offer free website migration assistance. This means they’ll help transfer your existing site to their servers without downtime or data loss.
7. WordPress Security
A robust WordPress security system is essential for protecting your site from threats. Quality hosts implement various security measures, including firewalls, malware scanning, and DDoS protection.
8. Performance and Reliability
When choosing a host, look for one that guarantees high performance and reliability. This often includes features like SSD storage for faster loading times and optimized server configurations specifically for WordPress sites.
My one blog’s traffic started growing rapidly after switching to a host that focused on performance—my page load times improved significantly!
9. Unlimited Bandwidth
Many hosting plans boast unlimited bandwidth, which means your site can handle high traffic without additional costs or throttling speeds during peak times.
This feature is vital if you plan on scaling your website or running promotional campaigns that might attract more visitors than usual.
10. Advanced Caching
Advanced caching solutions are essential for enhancing your site’s speed by storing static versions of your pages so they load faster for visitors.
My experience with caching plugins taught me just how much they can improve user experience and SEO rankings—something every blogger should consider seriously.
11. Money-Back Guarantee
Finally, a money-back guarantee gives you peace of mind when selecting a hosting provider. If things don’t work out as expected, you should be able to get your money back within a specified period—usually 30 days or more.
This safety net allowed me to try out different hosts without the fear of being stuck if they didn’t meet my expectations.
WordPress Hosting Benefits
1. Full Control
One of the standout advantages of WordPress hosting is the full control it gives you over your website. Unlike other website builders that may restrict your customization options, WordPress allows you to tailor your site exactly how you want it. You can choose from thousands of themes and plugins to create a unique user experience.
Let me explain with an example, A fashion brand wants to create an e-commerce website with a unique user experience. With WordPress hosting, they can choose from thousands of themes and plugins to customize their site's design, layout, and functionality. This level of control enables them to showcase their products in a way that reflects their brand's identity.
2. Speed
Speed is another critical factor where WordPress hosting shines. Many hosting providers optimize their servers specifically for WordPress, which means your site will load faster compared to generic shared hosting environments. Faster loading times not only improve user experience but also positively impact your SEO rankings.
3. Security
Security is paramount in today’s digital landscape, and WordPress hosting typically includes enhanced security features tailored specifically for WordPress sites. This includes regular malware scans, firewalls, and automatic updates that protect against vulnerabilities.
4. Uptime
A reliable website is essential for maintaining credibility and ensuring visitors can access your content whenever they want. Uptime refers to the percentage of time your website is operational and accessible online. Quality WordPress hosting providers often guarantee high uptime rates—typically 99.9% or higher.
Is WordPress Hosting Right for You?
Now that we’ve explored the benefits of WordPress hosting, you might be wondering if it’s the right choice for you. Here are some factors to consider:
- Your Technical Skills: If you're comfortable with technology and want full control over your site’s design and functionality, then WordPress hosting is an excellent option. However, if you prefer a more hands-off approach with limited customization, you might consider simpler website builders.
- Website Goals: Consider what you want to achieve with your website. If you're planning on running a blog or an e-commerce store that requires specific features and scalability, then investing in WordPress hosting will likely pay off in the long run.
- Budget: While WordPress hosting can be more expensive than shared hosting options, the benefits often outweigh the costs—especially if you're serious about growing your online presence. Look for hosts that offer flexible pricing plans to find one that fits your budget.
- Support Needs: If you're new to web development or managing a website, having access to expert support can be invaluable. Many managed WordPress hosts offer 24/7 support specifically trained in WordPress issues.
- Growth Potential: If you anticipate rapid growth or increased traffic over time, choosing a scalable WordPress hosting solution will allow you to upgrade easily as needed without major disruptions.
Pro Tip: Invest in managed WordPress hosting from the start. While it may seem more expensive, it saves time and offers peace of mind. Managed hosts handle technical aspects, allowing you to focus on content creation and audience engagement, with benefits like automatic updates and expert support.
5 Best WordPress Hosting Providers
| NO. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WP Engine | From $30/mo | Free SSL, Daily Backups, 24/7 Support | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | Bluehost | From $2.95/mo | Free Domain, Free SSL, 24/7 Support | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | Hostinger | From $1.99/mo | Free SSL, 24/7 Support | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | Namecheap | From $1.58/mo | Free Domain, Free SSL, 24/7 Support | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | Verpex | From $9.99/mo | Free SSL, Daily Backups, 24/7 Support | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
(viii) Free Hosting

What is Free Hosting?
Free hosting refers to web hosting services that are provided at no cost to the user. These services typically come with limited features and resources compared to paid hosting options.
Free hosting providers often cover their costs through advertisements displayed on users' websites or by offering limited support.
This type of hosting is generally suitable for personal projects, or for those who want to experiment with web development without financial commitment.
Free Hosting Pros and Cons
Pros:
- No Cost: The most obvious advantage is that it’s free! This makes it accessible for beginners or those on a tight budget.
- Ease of Use: Many free hosting platforms offer user-friendly interfaces, making it easy for newcomers to set up their websites without technical knowledge.
- Testing Ground: Free hosting can serve as a testing environment for new ideas or projects before committing to a paid plan.
Cons:
- Limited Resources: Free hosting often comes with restrictions on storage space, bandwidth, and features. This can hinder the growth of your website as traffic increases.
- Advertisements: Most free hosts display ads on your site, which can detract from your brand's professionalism and user experience.
- Lack of Support: Customer support is typically minimal or non-existent with free plans, leaving you to troubleshoot issues on your own.
- Unreliable Performance: Free hosts may experience downtime more frequently than paid services due to shared resources among many users
Free vs Paid Web Hosting
When comparing free and paid web hosting, several key differences emerge:
| Feature | Free Hosting | Paid Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | $0 | Varies (usually monthly or annually) |
| Advertisements | Often includes ads | No ads (unless you choose otherwise) |
| Support | Limited or no support | 24/7 customer support |
| Resources | Limited storage and bandwidth | Generally unlimited or higher limits |
| Domain Name | Subdomain (e.g., yoursite.freehost.com) | Custom domain (e.g., yoursite.com) |
| Performance | Less reliable due to shared resources | More stable performance |
When to Use Free Hosting
Free hosting can be a good choice in certain situations:
- Learning and Experimentation: If you’re new to web development or want to learn how to build a website without financial risk, free hosting is an excellent starting point.
- Personal Projects: For personal blogs or hobby websites where you don’t expect heavy traffic, free hosting can suffice.
- Testing Ideas: If you have a concept for a website but aren’t sure if it will gain traction, using free hosting allows you to test the waters without investment.
However, if you plan to grow your website into a business or expect significant traffic, transitioning to a paid plan sooner rather than later is advisable.
Limitations of Free Hosting
Despite its appeal, free hosting has notable limitations:
- Resource Constraints: Most free hosts impose strict limits on storage space and bandwidth. This can lead to slow loading times or even downtime if your site exceeds these limits.
- No Control Over Ads: You typically cannot control the ads displayed on your site. This can lead to irrelevant or inappropriate advertisements appearing alongside your content.
- Lack of Security Features: Free hosts often lack comprehensive security measures, making your site more vulnerable to attacks.
- Limited Scalability: As your website grows, you may find that free hosting cannot accommodate your needs, forcing you to switch providers later on.
Top 5 Free Web Hosting Services
| No. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | InfinityFree | Free | Unlimited Bandwidth, Free SSL, No Ads | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | 000Webhost | Free | 1GB Storage, Free SSL, No Ads | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | AwardSpace | Free | 1GB Storage, Free SSL, No Ads | 4.3/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | ByetHost | Free | 5GB Storage, Free SSL, No Ads | 4.2/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | FreeHosting | Free | 10GB Storage, Free SSL, No Ads | 4.1/5 | Visit Website |
III. How to Choose the Best Web Hosting Service Provider?
How to Choose Web Hosting?
When selecting a web hosting service, there are several factors to consider that will help you make an informed decision:
1. Determine Your Needs
Before you start looking for a hosting provider, assess your specific needs. Consider the following:
- Type of Website: Are you building a personal blog, an e-commerce site, or a portfolio? Different websites have different requirements.
- Traffic Expectations: Estimate how much traffic you expect. Higher traffic sites will require more resources.
- Technical Expertise: Are you comfortable managing technical aspects, or do you prefer a managed solution?
2. Understand Different Hosting Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of hosting available:
- Shared Hosting: Cost-effective and suitable for small websites; multiple sites share the same server resources.
- VPS Hosting: Offers more resources and flexibility; ideal for medium-sized businesses with moderate traffic.
- Dedicated Hosting: Provides an entire server for your website; best for large businesses or high-traffic sites.
- Cloud Hosting: Scalable and flexible, great for websites with fluctuating traffic.
Each type has its pros and cons, so choose one that aligns with your needs.
3. Evaluate Performance and Reliability
Look for providers that guarantee high uptime (ideally 99.9%) and fast loading speeds. Reading customer reviews can give you insights into their performance and reliability.
4. Check Customer Support
Reliable customer support is crucial, especially if you're not tech-savvy. Look for hosts that offer 24/7 support through various channels like chat, email, or phone.
5. Consider Scalability
Choose a host that allows you to upgrade your plan easily as your website grows. This flexibility can save you from having to migrate to a new host later on.
6. Read the Fine Print
Always check for hidden fees or terms in the contract. Some providers may have low introductory rates but charge significantly higher upon renewal or impose extra fees for certain features.
Understanding Hosting Costs
Web hosting costs can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of hosting and the features included in each plan. Here’s a breakdown of typical costs associated with various types of web hosting:
1. Shared Hosting Costs
Shared hosting is often the most affordable option:
- Initial Costs: Typically ranges from $2 to $5 per month.
- Renewal Costs: Can rise to $10 to $30 per month after the initial term.
This type is suitable for personal blogs or small business websites expecting low traffic.
2. VPS Hosting Costs
VPS hosting provides more resources than shared hosting:
- Cost Range: Generally falls between $20 to $100 per month.
- This option is ideal for growing websites that require better performance and control.
3. Dedicated Hosting Costs
Dedicated hosting is the most expensive option:
- Cost Range: Starts around $80 per month and can go up to $700 or more depending on server specifications.
- Best suited for large businesses or high-traffic websites needing maximum performance and security.
4. Cloud Hosting Costs
Cloud hosting offers scalability:
- Cost Range: Can vary significantly, often starting at around $30 per month and going up to $400 depending on resource usage.
- This is an excellent choice for businesses expecting rapid growth or fluctuating traffic patterns.
5. Hidden Costs
When budgeting for web hosting, don’t forget about additional expenses:
- Domain Name: Typically costs between $10-$20 per year.
- SSL Certificate: Often free with many hosts but can cost $20-$40 per year from some providers.
- Extensions and Themes: These can range from free to several hundred dollars depending on what you need.
Understanding these costs will help you make informed decisions when selecting a web hosting provider that fits your budget and needs.
IV. Web Hosting Comparison
Choosing the right web hosting provider is crucial for your online presence. Here we will compare multiple popular hosting services, based on their features, performance, pricing, and customer support. Our analysis aims to provide you with expert insights to help you make an informed decision.
1. Bluehost vs Hostinger: Which hosting is Better?
Bluehost: Founded in 2003, Bluehost is one of the largest hosting companies globally and is officially recommended by WordPress.org. It offers a range of hosting plans tailored for individuals and businesses.
Hostinger: Established in 2004, Hostinger is known for its budget-friendly options and high-performance hosting solutions. It has gained a reputation for excellent speed and uptime.
Bluehost vs Hostinger: Key Features Comparison
| Feature | Bluehost | Hostinger |
|---|---|---|
| 💰 Basic Price: | From $1.99/month | From $2.99/month |
| ⏱️ Uptime guarantee: | 99.9% | 99.9% |
| 🎟️ Coupons: | Bluehost coupon 75% OFF! | Hostinger coupon 75% OFF! |
| 💾 Storage space (from): | 10 GB SSD | 100 GB SSD |
| 🌐 Free domain (first year): | Yes | Yes |
| 🔒 Free SSL certificate: | Yes (first year) | Yes |
| 🚚 Site migration: | Free WordPress migration (1 site) or paid (up to 5 sites) | Free Automatic WordPress Website Migration |
| 🔄 Automated backups: | Daily Website Backups (Free 1st year), not with Basic Plan | Free (weekly) |
| 📧 Email accounts: | Free (up to 10 accounts) | Free (up to 100 accounts) |
| 📞 24/7 live support: | Yes | Yes |
| 💵 Money-back guarantee: | 30-day | 30-day |
| Visit Bluehost | Visit Hostinger |
Bluehost vs Hostinger Performance
| Metric | Bluehost | Hostinger |
|---|---|---|
| Loading Speed | ~400 ms | ~350 ms |
| Uptime | 99.98% | 99.90% |
| Data Center Locations | USA, Europe | USA, Europe, Asia |
Pricing Plans Comparison
Hostinger is cheaper than Bluehost, with prices for shared hosting starting at $2.54/month, while Bluehost is priced at $1.99/month.
But Overall, when considering pricing alone, Bluehost and Hostinger offer comparable rates for similar resources.. Bluehost’s entry price is lower and renewal price is higher but Hostinger’s entry price is higher and renewal is lower as compare to bluehost so it's cheaper than Bluehost’s.
Hosting Types Comparison
| Hosting Type | Bluehost | Hostinger |
|---|---|---|
| Shared hosting | ✓ | ✓ |
| WordPress hosting | ✓ | ✓ |
| WooCommerce hosting | ✓ | ✗ |
| Cloud hosting | ✓ | ✓ |
| VPS hosting | ✓ | ✓ |
| cPanel hosting | ✓ | ✓ |
| Minecraft hosting | ✗ | ✓ |
| CyberPanel hosting | ✗ | ✓ |
| Dedicated hosting | ✓ | ✗ |
| Visit Bluehost | Visit Hostinger |
Customer Support
| Feature | Bluehost | Hostinger |
|---|---|---|
| 24/7 live chat | ✓ | ✓ |
| Phone support | ✓ | ✗ |
| Email support | ✓ | ✓ |
| Guides and tutorials | ✓ | ✓ |
Hostinger vs Bluehost: Which One Should You Choose?
Choose Bluehost if you prioritize customer support, ease of use, and WordPress integration.
Opt for Hostinger if you are looking for budget-friendly plans without compromising on performance.
| Feature | Bluehost | Hostinger | Verdict |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Both Bluehost and Hostinger offer competitive pricing, but Bluehost's cheapest plan is slightly more affordable. |
| Ease of use | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Both providers are user-friendly, but Bluehost offers additional tools like staging that can be very helpful. |
| Performance | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Hostinger outperforms Bluehost in terms of speed and reliability, making it the better choice for performance. |
| Security | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Both providers offer basic security features, but for advanced security, additional costs are involved. |
| Support | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Bluehost offers faster response times, but Hostinger's support agents are generally more knowledgeable. |
2. Hostgator vs Bluehost: Which one is Better?
Bluehost and HostGator are two of the most prominent web hosting providers available today. Each has its unique strengths and weaknesses, catering to different user needs.
In this comparison of Bluehost vs. HostGator, we will evaluate both hosting providers across several categories, including pricing, performance, ease of use, customer support options, and website security features.
Read on to discover which host may be the better choice for your website.
Hostgator vs Bluehost: Key Features Comparison
| Feature | HostGator | Bluehost |
|---|---|---|
| 💰 Price | From $3.75/month | From $1.99/month |
| ⏰ Uptime guarantee | 99.9% | 99.9% |
| 🎟️ Coupons | Hostgator coupon 73% OFF! | Bluehost coupon 75% OFF! |
| 💾 Storage space (from) | 10 GB SSD | 10 GB SSD |
| 🌐 Free domain (first year) | Yes (first year) | Yes |
| 🔒 Free SSL certificate | Yes | Yes (first year) |
| 🚚 Site migration | 1 free WordPress/cPanel migration and inter-server migration | Free WordPress migration (1 site) or paid (up to 5 sites) |
| 💽 Automated backups | Yes (paid) | Daily Website Backups (Free 1st year), not with Basic Plan |
| 📧 Email accounts | Yes (unlimited accounts) | Free (up to 10 accounts) |
| 📞 24/7 live support | Yes | Yes |
| 💵 Money-back guarantee | 30-day | 30-day |
| Visit Hostgator | Visit Bluehost |
Hostgator vs Bluehost Performance
| Metric | Hostgator | Bluehost |
|---|---|---|
| Loading Speed | ~350 ms | ~400 ms |
| Uptime | 99.9% | 99.9% |
| Data Center Locations | U.S. | USA, Europe |
Pricing Plans
Bluehost and HostGator are two leading web hosting providers, each with unique pricing structures and offerings.
In this comparison, we will break down their shared hosting plans to help you understand which might be the better option for your needs.
- Bluehost offers shared hosting plans starting at $1.99/month, while HostGator begins at $3.75/month.
- Although Bluehost's plans can go up to $8.99/month, HostGator's highest tier stops at $6.25/month, making HostGator a more economical choice overall.
Other hosting options provided by both providers are almost similar:
| Hosting Type | HostGator | Bluehost |
|---|---|---|
| Shared hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| WordPress hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| WooCommerce hosting | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Cloud hosting | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| VPS hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Dedicated hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Visit Hostgator | Visit Bluehost |
Both Bluehost and HostGator's promotional rates apply to 36-month subscriptions, with renewal prices increasing significantly after the initial term:
- Bluehost Renewal Rates: Start from approximately $8.99/month.
- HostGator Renewal Rates: Begin around $6.25/month, making it a more budget-friendly option in the long run.
HostGator vs Bluehost: which offers better security?
| Features | HostGator | Bluehost |
|---|---|---|
| Free SSL | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| DDoS protection | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Automatic backups | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| 2FA account security | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Spam protection | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Monitoring software | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Visit Hostgator | Visit Bluehost |
HostGator vs Bluehost: Customer Support
| Feature | HostGator | Bluehost |
|---|---|---|
| 24/7 Live Chat | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| ❌ No | ❌ No | |
| Phone Line | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Knowledge Base | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| FAQs | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
Hostgator vs Bluehost: Which is Better?
Both Bluehost and HostGator have established themselves as leading web hosting providers with unique offerings:
- If you're a beginner looking for a user-friendly experience with excellent WordPress integration and strong performance metrics, Bluehost may be the better choice.
- For users who prioritize flexible pricing options and extensive features for scalability, particularly for growing businesses, HostGator could be more suitable.
| Feature | HostGator | Bluehost | Verdict |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | HostGator is generally cheaper, especially for higher-tier plans and renewals. |
| Ease of use | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Both are user-friendly, but Bluehost offers more tools for website success. |
| Performance | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | HostGator excels in loading speed and traffic handling, while Bluehost has better response times. |
| Security | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Both have paid security tools, but Bluehost makes setup easier. |
| Support | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Bluehost provides more accurate support, while HostGator may require multiple interactions. |
HostGator and Bluehost are both reputable web hosting providers, each offering distinct advantages. HostGator is known for its affordability and straightforward user interface, providing reliable performance, especially in site loading speed and traffic management. However, it features a basic security suite.
On the other hand, Bluehost presents competitive pricing with a more intuitive control panel that integrates cPanel, along with a variety of useful tools. Its performance is commendable, boasting excellent uptime and response times.
While both hosts have their merits, Bluehost stands out as the superior option overall. The control panel is easier to navigate, offering more comprehensive tools for managing site security. Additionally, Bluehost's customer support is often noted as being more efficient and responsive compared to HostGator's.
3. Hostinger vs Hostgator: Which hosting delivers better services?
Hostinger and HostGator are popular web hosting providers offering affordable and reliable solutions.
In this review, we'll explore the details of each provider's pricing, ease of use, performance, security, and customer support.
By the end of this comparison, you'll know which host is the best fit for your website's needs.
Hostinger vs Hostgator: Key Features Comparison
| Feature | Hostinger | HostGator |
|---|---|---|
| Price 💰 | From $2.99/month | From $3.75/month |
| Uptime guarantee ⏱️ | 99.9% | 99.9% |
| Coupons 🎟️ | Hostinger coupon 78% OFF | Hostgator Web Hosting Coupons |
| Storage space (from) 💾 | 100 GB SSD | 10 GB SSD |
| Free domain (first year) 🌐 | Yes | Yes (first year) |
| Free SSL certificate 🔒 | Yes | Yes |
| Site migration 🚚 | Free Automatic WordPress Website Migration | 1 free WordPress/cPanel migration and inter-server migration |
| Automated backups 💾 | Free (weekly) | Yes (paid) |
| Email accounts 📧 | Free (up to 100 accounts) | Yes (unlimited accounts) |
| 24/7 live support 📞 | Yes | Yes |
| Money-back guarantee 💵 | 30-day | 30-day |
| Visit Hostinger | Visit Hostgator |
Hostinger vs Hostgator Performance
| Metric | Hostinger | Hostgator |
|---|---|---|
| Loading Speed | ~511 ms | ~525 ms |
| Uptime | 99.9% | 99.9% |
Pricing Plan
One of the first things that caught my eye was the pricing. As a newbie blogger, I was on a tight budget. Here’s how they stack up:
Hostinger takes the lead in affordability, with plans starting at just $2.54/month. HostGator's cheapest shared hosting plan, on the other hand, costs $3.75/month.
Both providers offer a range of scalable hosting solutions, including:
| Hosting Type | Hostinger | HostGator |
|---|---|---|
| Shared hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| WordPress hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Cloud hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| VPS hosting | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| cPanel hosting | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Minecraft hosting | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| CyberPanel hosting | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Dedicated hosting | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Visit Hostinger | Visit Hostgator |
Hostinger offers 2 shared hosting and 1 cloud hosting plan, starting at $2.54/month. The Premium plan is the most popular, offering hosting for 100 websites, 100GB storage, and a free Domain.
Hostinger provides a 30-day money-back guarantee, allowing you to cancel and receive a full refund within this timeframe. Note that domain names are non-refundable.
HostGator has 3 shared hosting plans, priced between $3.75/month and $6.25/month. The Baby plan is recommended as the best value, offering unlimited website hosting and lower renewal rates.
HostGator also offers a 30-day money-back guarantee, with the same exception: domain names are not refundable.
In a nutshell, Hostinger wins on price, with plans starting at $2.54/month, beating HostGator's $3.75/month. Affordability gives Hostinger the edge.
Hostinger vs HostGator: Which One is Easy to Use
Both Hostinger and HostGator cater to beginners with simple interfaces, but they use different management systems.
Hostinger:
-
Offers a single native hPanel for easy management
-
Automatic account setup wizard for quick setup
-
hPanel provides access to various tools like domain names, SSL configuration, email accounts, and more
HostGator:
-
Uses a combination of native interface and cPanel
-
Native interface handles basic tasks like billing and support
-
cPanel offers advanced tools like email accounts, file management, databases, and security features
-
Softaculous Installer app for easy CMS installation
Both Hostinger and HostGator offer user-friendly interfaces, but Hostinger takes the lead with its intuitive custom control panel (hPanel) and automatic setup wizard, making it incredibly easy for beginners to manage their websites. Hostinger's hands-on approach gives it the edge in this round!
Hostinger vs HostGator: which offers better security?
| Feature | Hostinger | HostGator |
|---|---|---|
| Free SSL Certificate 🔒 | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| DDoS Protection 🛡️ | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Automatic Backups 💾 | ✅ Weekly backups included | ❌ No automatic backups; paid add-ons needed |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) 🔐 | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Visit Hostinger | Visit Hostgator |
Hostinger vs HostGator: Customer Support
Having reliable customer support can save you from many headaches down the line. Here’s how they stack up:
- Hostinger offers 24/7 live chat support that I found to be responsive and helpful.
- HostGator also provides 24/7 support but has received mixed reviews regarding response times and effectiveness.
In my experience, both services were decent, but I often felt that Hostinger's support was quicker to resolve issues.
Hostinger vs HostGator: Final Recommendations
This brings us to the conclusion of our comparison between HostGator and Hostinger. While both hosting providers have their strengths, Hostinger stands out in several key areas. It offers better performance metrics at more affordable prices, which gives it a significant edge over HostGator.
| Feature | Hostinger | HostGator | Verdict |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price 💰 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Hostinger offers a more budget-friendly option, starting at just $2.99/month, compared to HostGator's $3.75/month. |
| Ease of use 🖥️ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Both are user-friendly, but Hostinger's custom hPanel is particularly beginner-friendly, while HostGator uses the familiar cPanel interface. |
| Performance 🚀 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Hostinger boasts a perfect 99.9% uptime, with faster response and load times compared to HostGator. |
| Security 🔒 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Hostinger includes essential security features like SSL, automatic backups, and 2FA in all plans, whereas HostGator lacks 2FA but offers additional paid security options. |
| Support 📞 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Both provide 24/7 live chat support. Hostinger also offers email support, while HostGator provides phone support. Both have knowledgeable and responsive support teams. |
With lower initial costs, a more user-friendly control panel, responsive customer support, and slightly superior performance, Hostinger emerges as the clear winner. This makes it an excellent choice for those on a budget who still want reliable hosting to establish their online presence.
V. Advanced Hosting Features and Technologies
(i) Server Technologies
Different server technologies can significantly impact your website's performance, scalability, and overall user experience.
In this section, we’ll explore various server technologies, comparing popular options like Apache, NGINX, LiteSpeed, and others, while also discussing the differences between Linux and Windows hosting and the benefits of PHP MySQL hosting.
Server Technologies for Hosting
Server technologies refer to the software and hardware solutions that manage how websites are hosted and served to users. The choice of server technology can influence factors such as speed, reliability, and resource management. Here are some of the most common server technologies used in web hosting today:
1. Apache
Apache is one of the oldest and most widely used web servers globally. It employs a process-driven architecture that creates a new process for each request. This can lead to stability since individual processes are isolated; however, it can be resource-intensive under heavy loads. Apache excels in handling dynamic content and offers extensive customization through its module system.
2. NGINX
NGINX is known for its high performance and efficiency, particularly in serving static content. It uses an event-driven architecture that allows it to handle multiple connections simultaneously with minimal resource consumption. This makes NGINX a preferred choice for high-traffic websites and applications requiring scalability.
3. LiteSpeed
LiteSpeed is a commercial web server that offers high performance and security features. It’s particularly effective at serving dynamic content quickly and can be a drop-in replacement for Apache, supporting .htaccess files. LiteSpeed also includes built-in caching capabilities which enhance performance.
4. OpenLiteSpeed
OpenLiteSpeed is the open-source version of LiteSpeed, providing many of the same benefits without the associated costs. It’s lightweight and optimized for speed but may lack some advanced features found in its commercial counterpart.
5. Microsoft IIS
Microsoft's Internet Information Services (IIS) is a web server designed for Windows environments. It integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products and technologies, making it ideal for businesses heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Apache vs NGINX Hosting
When comparing Apache and NGINX, several factors come into play:
| Feature | Apache | NGINX |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Process-driven | Event-driven |
| Performance | Slower with static content | Faster with static content |
| Dynamic Content | Handles internally | Requires external processors (e.g., FastCGI) |
| Configuration | Flexible with .htaccess files | Simpler configuration but less flexible |
| Resource Usage | More memory-intensive | More efficient under load |
In general, NGINX is preferred for high-traffic sites due to its ability to handle many connections efficiently, while Apache remains popular for sites needing extensive customization.
NGINX vs LiteSpeed
When comparing NGINX vs LiteSpeed, several factors come into play:
| Feature | NGINX | LiteSpeed |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for static content | Superior performance for dynamic content |
| Caching | Requires additional configuration | Built-in caching features |
| Compatibility | Works well with PHP via FastCGI | Supports .htaccess files |
| Cost | Free and open-source | Commercial license required for full features |
| Ease of Use | Requires some configuration knowledge | User-friendly with many optimizations |
| Security | Basic security features | Advanced security options available |
Ultimately, the choice between NGINX and LiteSpeed will depend on specific use cases—if performance with dynamic content is crucial, LiteSpeed might be the better option.
LiteSpeed vs OpenLiteSpeed
When comparing LiteSpeed vs OpenLiteSpeed, several factors come into play:
| Feature | LiteSpeed | OpenLiteSpeed |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Paid (commercial license) | Free and open-source |
| Performance | High performance with optimizations | Good performance but fewer optimizations than LiteSpeed |
| Features | Advanced features (security, caching) | Basic features |
| Support | Professional support available | Community support only |
| Options | ||
| Compatibility | Compatible with .htaccess files | Similar compatibility |
For many users looking for cost-effective solutions without sacrificing too much performance, OpenLiteSpeed remains an excellent choice.
Linux vs Windows Hosting
When comparing Linux vs Windows hosting, several factors come into play:
| Feature | Linux Hosting | Windows Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Operating System | Open-source Linux distributions | Proprietary Microsoft Windows |
| Performance | Stable and efficient | Good performance, especially for .NET applications |
| Technologies Supported | PHP, MySQL, Perl, Python | ASP.NET, MSSQL |
| Control Panel Options | cPanel, Plesk | Plesk |
| Community Support | Large community support | Limited to Microsoft resources |
For many users looking for cost-effective solutions without sacrificing too much performance, OpenLiteSpeed remains an excellent choice.
PHP MySQL Hosting
PHP MySQL hosting refers to hosting services optimized for running PHP applications backed by MySQL databases. This combination is widely used for dynamic websites due to:
- Performance: PHP works efficiently with MySQL to deliver fast database-driven applications.
- Community Support: Both PHP and MySQL have large communities providing extensive resources, documentation, and support.
- Compatibility: Most hosting providers offer plans specifically tailored for PHP MySQL applications.
Choosing a host that specializes in PHP MySQL can enhance your website's performance and reliability.
(ii) Control Panels/WHM
What is Web Hosting Control Panel?
A web hosting control panel is a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to manage their web hosting accounts and servers easily.
It provides a centralized dashboard where users can perform various tasks, such as managing files, databases, email accounts, and domain settings without needing extensive technical knowledge. Popular examples of control panels include cPanel, Plesk, and DirectAdmin.
Purpose of a Web Hosting Control Panel
The primary purpose of a web hosting control panel is to streamline the management of web hosting services. Here are some key functions it serves:
- Simplifies Server Management: Control panels provide an intuitive interface that makes it easy for users to manage their servers and hosted services. This reduces the complexity associated with server administration.
- Enhances User Accessibility: By offering a user-friendly environment, control panels enable individuals without technical expertise to perform essential tasks related to their websites and hosting accounts.
- Centralizes Administrative Tasks: Users can manage multiple aspects of their hosting environment from one location, including monitoring resource usage, configuring security settings, and backing up data.
- Improves Efficiency: With automation tools and straightforward navigation, control panels save time and resources for users managing their websites.
Key Features of a Hosting Control Panel
Web hosting control panels come equipped with various features that facilitate effective management of websites and servers. Here are some key features commonly found in these control panels:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| File Management | Allows users to upload, delete, and organize files on their server directly through the panel. |
| Database Management | Provides tools for creating and managing MySQL or PostgreSQL databases, including access to phpMyAdmin. |
| Email Management | Enables users to create and manage email accounts associated with their domain names, set up forwarders, and configure spam filters. |
| DNS Management | Offers options to edit or add DNS records for domain names easily. |
| Backup Solutions | Facilitates automated backups or manual backup options to ensure data safety. |
| Security Features | Includes tools for managing SSL certificates, setting up firewalls, and monitoring for potential threats. |
| Resource Monitoring | Allows users to track server resource usage (CPU, RAM, disk space) in real-time. |
| Software Installation | Simplifies the installation of applications like WordPress or content management systems with one-click installers. |
| User Account Management | Supports creating and managing multiple user accounts with varying access levels (e.g., admin, user). |
| Remote Access | Provides remote access capabilities so users can manage their servers from anywhere with an internet connection. |
Why Do you Need a Web Hosting Control Panel?
1. Simplifies Server Management
One of the primary reasons to use a web hosting control panel is that it significantly simplifies server management. Without a control panel, managing server configurations, application deployments, and security settings can be complex and daunting, especially for those without extensive technical knowledge.
Control panels streamline these processes by providing user-friendly interfaces that allow users to manage their servers with ease.For example, tasks like file management, database creation, and email account setup can be performed through simple clicks rather than complicated command-line instructions.
This ease of use allows users to focus on their projects rather than getting bogged down by technical details.
2. User-friendly Interface
Web hosting control panels are designed with user experience in mind. They typically feature intuitive dashboards that allow users to navigate through various functionalities effortlessly.
This user-friendly interface makes it easy to perform essential tasks such as managing domains, monitoring server performance, and configuring security settings without needing advanced technical skills.
The simplicity of these interfaces often includes drag-and-drop functionality for file management and one-click installations for applications like WordPress, which greatly enhances the overall user experience.
This accessibility encourages more users to take control of their web hosting environments confidently.
3. Time and Resource-saving
Using a web hosting control panel can save significant time and resources. Many routine tasks can be automated through the control panel, reducing the need for manual intervention.
For instance, automated backups can be scheduled to ensure data safety without requiring constant oversight.Additionally, features like task automation allow users to execute commands or scripts at specified times, further streamlining operations.
By minimizing the time spent on repetitive tasks, users can allocate their efforts toward more critical aspects of their projects, such as content creation and user engagement.
4. Security Features
Security is a major concern for any website owner, and web hosting control panels often come equipped with robust security features. These may include tools for managing SSL certificates, setting up firewalls, and monitoring for potential threats.
Control panels also facilitate easier management of user permissions and access levels, ensuring that only authorized individuals can make critical changes to the server settings.
By centralizing security configurations within an easy-to-use interface, control panels help maintain a secure hosting environment without overwhelming users with complex security protocols.
Popular Web Hosting Control Panels
Web hosting control panels are essential tools that simplify the management of web hosting services. They provide user-friendly interfaces for managing various aspects of web hosting, making it easier for users to perform tasks without extensive technical knowledge.
Here’s an overview of some popular web hosting control panels, along with their key features.
1. CloudPanel
CloudPanel is a modern control panel designed for managing cloud servers efficiently. It offers a clean and intuitive interface, making it easy to deploy applications and manage resources.
Key Features of CloudPanel:
- One-Click Application Installation: Easily install popular applications like WordPress or Joomla.
- Server Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of server performance and resource usage.
- Multiple Server Management: Manage multiple servers from a single dashboard.
- Automated Backups: Schedule regular backups to ensure data safety.
- SSL Management: Simplified management of SSL certificates, including Let's Encrypt integration.
2. DirectAdmin
DirectAdmin is a robust web hosting control panel known for its speed and efficiency. It supports various Linux distributions and offers a wide range of features.
Key Features of DirectAdmin Include:
- Multiple Access Levels: Administrator, Reseller, and User levels for versatile management.
- Comprehensive System Usage Statistics: Provides insights into server health and performance.
- Automatic SSL Management: Automates the installation and renewal of SSL certificates.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design that simplifies navigation and task execution.
- Resource Throttling: Ability to throttle CPU, RAM, and I/O resources per user.
3. Virtualmin
Virtualmin is an open-source control panel that provides powerful features for managing virtual hosts and servers. It is suitable for both beginners and advanced users.
Key Features of Virtualmin Include:
- Multi-domain Management: Easily manage multiple domains from a single interface.
- Backup and Restore Options: Comprehensive backup solutions for data safety.
- Customizable User Roles: Define user roles with specific permissions for better security.
- Integrated File Manager: Manage files directly from the control panel.
- Support for Multiple Linux Distributions: Compatible with various Linux operating systems.
4. cPanel
cPanel is one of the most widely used web hosting control panels, known for its extensive features and user-friendly interface.
Key cPanel Features Include:
- File Manager: Easy file uploads, deletions, and organization through a graphical interface.
- Database Management: Tools like phpMyAdmin for managing MySQL databases effortlessly.
- Email Management: Create and manage email accounts associated with your domain.
- One-Click Installers: Quickly install popular applications with minimal effort.
- Security Features: Built-in tools for managing SSL certificates and security settings.
5. Plesk
Plesk is another popular control panel that supports both Linux and Windows hosting environments. It offers a wide range of features tailored to different user needs.
Key Plesk Features Include:
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design that simplifies server management tasks.
- Multi-platform Support: Compatible with both Windows and Linux servers.
- Security Tools: Integrated security features like firewalls, fail2ban, and SSL management.
- Application Catalog: Access to a wide range of applications that can be installed easily.
- Backup Manager: Automated backup solutions to protect website data.
6. Webmin
Webmin is a web-based interface for system administration on Unix-like systems. It allows users to manage their servers without needing command-line knowledge.
Key Features of Webmin Include:
- Modular Design: Supports various modules for different administrative tasks (e.g., DNS management, file sharing).
- User Management: Easily create and manage user accounts with specific permissions.
- System Monitoring Tools: Monitor system performance metrics directly from the dashboard.
- Backup Configuration Options: Tools for backing up configuration files and system settings.
- Extensive Documentation: Comprehensive resources available to assist users in navigating the platform.
What is CyberPanel?
CyberPanel is an open-source web hosting control panel that allows users to manage their web hosting servers with ease. It is built on top of the LiteSpeed Web Server, which is known for its high performance and resource efficiency. CyberPanel enables users to create and manage websites, handle DNS settings, install SSL certificates, and much more—all from a user-friendly interface.
Key Features of CyberPanel
- LiteSpeed Web Server: CyberPanel utilizes LiteSpeed Web Server, providing excellent performance for dynamic websites while conserving server resources.
- One-Click Application Installer: Users can easily install popular applications like WordPress and Drupal with just one click, streamlining the setup process.
- SSL Management: CyberPanel simplifies SSL certificate management by offering a one-click installation for Let's Encrypt certificates, along with automatic renewal features.
- Database Management: It includes tools for managing databases through phpMyAdmin, making it easy to create, modify, and delete databases as needed.
- DNS Management: Users can manage DNS records directly through the control panel, including integration with Cloudflare for enhanced performance and security.
- Email Support: CyberPanel supports email management, allowing users to create email accounts and access webmail powered by Rainloop.
- Automatic Backups: The platform offers automated backup solutions, including real-time incremental backups to ensure data safety.
- Staging/Clone Site Functionality: This feature allows users to create staging environments or clone existing sites for testing purposes before making changes live.
- Git Deployment: Developers can deploy applications directly from Git repositories, enhancing workflow efficiency.
- Containerization Support: CyberPanel supports Docker containers, enabling users to run applications in isolated environments.
- User Management: Administrators can manage user roles and permissions effectively within the control panel.
- File Manager: A built-in file manager allows users to upload, download, edit, and manage files directly from the interface.
- ModSecurity Integration: Provides enhanced security through ModSecurity, which acts as a web application firewall to protect against various online threats.
- Server Monitoring: Users can monitor server performance metrics through a clean dashboard that displays essential information about resource usage and health.
What is WHM and It's Features?
WHM (WebHost Manager) is an administrative control panel that allows users to manage their hosting environment effectively. It enables the creation, deletion, and management of cPanel accounts, providing a comprehensive suite of tools for server administration.
WHM is essential for web hosting companies and resellers who need to oversee multiple customer accounts while maintaining high levels of security and performance.
Features of WHM
WHM comes equipped with numerous features designed to facilitate server management and enhance user experience. Here are some of the key features:
1. Account Management
- Create, Delete, or Suspend Accounts: WHM allows administrators to create new cPanel accounts for customers easily. If an account needs to be suspended or deleted due to violations or inactivity, this can be done quickly through the interface.
- Manage Bandwidth and Disk Space: Administrators can monitor and adjust the bandwidth and storage allocated to each account, ensuring optimal resource usage.
2. Monitoring and Reporting
- Server Activity Monitoring: WHM provides tools to monitor server performance, including the Process Manager, which tracks running processes, and the Service Manager for managing background services.
- Disk Usage Statistics: Users can view current disk usage statistics to understand resource allocation across accounts.
3. Customization Options
- Branding Capabilities: Resellers can customize the WHM interface with their branding elements, such as logos and documentation links. This feature enhances the customer experience by providing a cohesive brand identity.
- Default Page Configuration: When creating new accounts, administrators can set a default page that users will see upon logging in.
4. Security Features
- SSL Certificate Management: WHM allows users to install and manage SSL certificates for secure connections, which is crucial for e-commerce websites.
- cPHulk Brute Force Protection: This feature helps protect against unauthorized access attempts by blocking IP addresses after multiple failed login attempts.
5. File Transfer Capabilities
- Transfer Files Between Servers: WHM enables administrators to transfer files between remote servers easily, making it convenient for migrating customer websites or data.
6. Reseller Management
- Create Reseller Accounts: Hosting providers can create reseller accounts that allow other users to sell hosting services under their brand.
- Market Provider Manager: This feature lets resellers manage products available for purchase through their cPanel accounts.
7. Feature Management
- Control Feature Lists: Administrators can define which features are available to different cPanel accounts by creating custom feature lists. This allows for tailored service offerings based on customer needs.
8. Support Request Management
- Customer Support Configuration: WHM allows administrators to configure how support requests are handled through cPanel, streamlining communication between customers and support teams.
Here’s a detailed comparison of cPanel with Plesk, WHM, CloudPanel, and CyberPanel presented in table format. This will help you understand the differences and similarities between these popular web hosting control panels.
cPanel vs Plesk
| Feature | cPanel | Plesk |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Primarily Linux-based | Supports both Linux and Windows |
| User Interface | Cluttered but customizable | Streamlined and modern |
| Performance | Generally faster loading times | Slightly slower but offers flexibility |
| Account Management | Separate logins for cPanel and WHM | Unified login for both user and admin tasks |
| Security Features | SSL management, IP blocking | Fail2ban, email spam filters |
| Backup Options | Manual restoration from backup files | Automated and scheduled backups |
| App Support | Supports various apps via Softaculous | Extensive app support, including Docker |
| obile Accessibility | No dedicated mobile app | Mobile app available for management |
cPanel vs WHM
| Feature | cPanel | WHM (WebHost Manager) |
|---|---|---|
| Target Users | End-users (website owners) | Server administrators and resellers |
| Account Management | Manages individual user accounts | Manages multiple cPanel accounts |
| Interface Type | User-friendly graphical interface | Administrative interface for server tasks |
| Resource Monitoring | Limited to user account stats | Comprehensive server resource monitoring |
| Security Features | Basic security tools | Advanced security settings for the server |
| Backup Options | User-initiated backups | Server-wide backup options |
cPanel vs CloudPanel
| Feature | cPanel | CloudPanel |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Linux-based | Cloud-based (supports various OS) |
| User Interface | Traditional interface | Modern, clean interface |
| Performance Optimization | Focused on shared hosting | Optimized for cloud environments |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable for cloud applications |
| Backup Solutions | Manual backup management | Automated backups available |
| App Support | Extensive app support through Softaculous | One-click installations for popular apps |
cPanel vs CyberPanel
| Feature | cPanel | CyberPanel |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Linux-based | Linux-based (OpenLiteSpeed) |
| User Interface | Classic graphical interface | Modern interface with a focus on speed |
| Web Server Support | Primarily Apache | OpenLiteSpeed with enhanced performance |
| Performance Optimization | Good performance but resource-intensive | Lightweight and optimized for speed |
| Backup Options | Manual backup management | Automated backup solutions |
| Security Features | SSL management, IP blocking | Built-in firewall and security features |
(iii) Domain Management and DNS
Whether you're starting a blog, launching a business, or creating a personal website, the right domain name can make a significant difference in how your audience perceives you.
Let's dive into what a domain name is, the different types, who manages them, and how to register one.
What is a domain name?
A domain name is essentially the address of your website on the internet. It’s what people type into their browser to find your site. For example, when you type “google.com,” you’re entering the domain name for Google’s website.
The domain name consists of two main parts: the second-level domain (SLD) and the top-level domain (TLD). In “google.com,” "google" is the SLD, and ".com" is the TLD.
When I first started my blog, I remember feeling overwhelmed by all the technical jargon surrounding domain names.
I thought I had to choose something super creative or unique to stand out. But honestly, what matters most is that the name is easy to remember and reflects what your site is about.
Types of Domains
There are several types of domains you should be aware of:
- Top-Level Domains (TLDs): This is the part that comes after the last dot in
a
domain name. Common TLDs include:
- Generic Top-Level Domains (gTLDs) like .com, .net, and .org.
- Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs) which are specific to countries, like .uk for the United Kingdom or .ca for Canada.
- Sponsored Top-Level Domains (sTLDs) which are restricted to specific groups or organizations, such as .edu for educational institutions or .gov for government entities.
- Second-Level Domains (SLDs): This is the part before the TLD. It usually represents your brand or organization.
- Subdomains: These are extensions of your main domain that help organize content. For instance, if you have a blog section on your site, it might look like blog.yoursite.com.
- Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs): These allow users to register domain names in non-Latin scripts, making the internet more accessible globally.
Who manages domain names?
Domain names are managed by organizations known as registrars. These registrars are accredited by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), which oversees the entire domain name system globally.
When you register a domain through a registrar like GoDaddy or Namecheap, you’re essentially renting that name for a specified period—usually one year at a time.I remember my first experience with a registrar was quite eye-opening.
I thought it would be straightforward, but there were so many options! From privacy protection to email hosting—there's a lot to consider beyond just securing the name itself.
What is DNS?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is like the phonebook of the internet. It translates human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
When you enter a URL in your browser, DNS servers take care of finding the corresponding IP address so that you can access the website.I didn’t fully grasp how DNS worked until I faced an issue with my site not loading properly.
After some digging, I discovered that my DNS settings were misconfigured! It was a learning moment that highlighted just how crucial DNS management is for keeping your website running smoothly.
What is DNS Management for Hosting?
DNS management refers to controlling and maintaining your DNS records through your hosting provider or registrar. This includes setting up records like A records (which point your domain to an IP address), CNAME records (which allow you to alias one domain name to another), and MX records (which direct email traffic).
Proper DNS management ensures that visitors can reach your site without issues. If you change hosting providers or need to set up email services under your domain, you'll need to update these records accordingly.
When I changed my hosting provider once, I didn’t realize how important it was to update my DNS settings immediately. My site went down for several hours because I forgot this crucial step! It taught me to always double-check my DNS settings whenever making changes.
How to Decide Domain Name?
Choosing the right domain name can feel daunting but here are some tips:
- Keep it short and memorable: Aim for something easy to spell and pronounce.
- Use keywords: If possible, include relevant keywords related to your niche.
- Avoid numbers and hyphens: These can confuse users when they try to remember your URL.
- Check availability: Use tools like Namecheap or GoDaddy to see if your desired name is available.
I once spent weeks brainstorming what I thought was an original name only to find out it was already taken! Don’t forget to check social media platforms too; consistency across platforms helps with branding.
How to Register a Domain for Your Website?
Registering a domain is fairly straightforward:
- Choose a registrar: Popular options include GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains.
- Search for your desired domain name: Use their search tool.
- Select your TLD: Decide if you want .com, .org, etc.
- Fill out registration information: This usually includes providing contact details.
- Complete payment: Domains typically cost between $10-$20 per year.
- Set up DNS settings: Configure these according to your hosting provider’s instructions.
When I registered my first domain, I felt accomplished! It was like taking ownership of my little corner of the internet. Just remember—once you register it, keep track of renewal dates so you don’t lose it!
How to Connect a Domain to Your Hosting Provider?
Connecting a domain name to your hosting provider is an essential step in getting your website up and running. Let’s say you’ve purchased a domain from Namecheap and you want to connect it to your Bluehost hosting account.
This process might sound a bit technical at first, but I assure you it’s quite straightforward once you break it down into steps. I remember when I did this; I felt a mix of excitement and nervousness, but it turned out to be easier than I expected.
Step 1: Gather Your Information
Before diving into the connection process, you'll need to know the nameservers for Bluehost. These are typically:
- ns1.bluehost.com
- ns2.bluehost.com
Having these handy will make the next steps much smoother. When I first set this up, I had to search around for these nameservers, which added unnecessary time to my project. So, trust me, save yourself the hassle and note them down right away!
Step 2: Log Into Your Namecheap Account
- Start by logging into your Namecheap account. Once you're in, navigate to the Domain List on the left sidebar.
- Here, you’ll see all the domains you own. Find the domain you want to connect to Bluehost and click on the Manage button next to it.
I remember feeling a bit overwhelmed by all the options available in my Namecheap dashboard at first. It can look cluttered if you're not familiar with it, but don’t let that discourage you!
Step 3: Change Your Nameservers
Once you're on the domain management page:
- Scroll down until you find the Nameservers section.
- Click on the dropdown menu and select Custom DNS.
- Now, enter the Bluehost nameservers:
- For Nameserver 1, input ns1.bluehost.com.
- For Nameserver 2, input ns2.bluehost.com.
After entering these details, click on the green checkmark to save your changes.I recall my first attempt at this step; I accidentally typed in an incorrect nameserver! My website didn’t connect properly for hours until I figured out what went wrong. So double-check those entries!
Step 4: Wait for DNS Propagation
After changing your nameservers, it’s important to know that it can take some time for these changes to take effect—sometimes up to 48 hours. This is due to something called DNS propagation, which is just a fancy way of saying that it takes time for all internet service providers around the world to update their records.In my case, I was so eager that I kept checking my website every few minutes! It was a lesson in patience—just because you’ve made changes doesn’t mean they’ll show up instantly.
Step 5: Verify Your Domain in Bluehost
While waiting for DNS propagation, you can prepare on the Bluehost side:
- Log into your Bluehost account.
- Navigate to the Domains section from your dashboard.
- Click on Assign a Domain.
Here’s where you'll input your newly connected domain name. Bluehost will verify ownership based on the nameservers you've set up in Namecheap.I remember feeling a rush of excitement when my domain was finally verified! It felt like a huge milestone in my website-building journey.
Step 6: Set Up Your Website
Once your domain is connected and verified, you can start setting up your website! If you're using WordPress or another CMS (Content Management System), you can install it directly through Bluehost's interface.When I first set up WordPress on my site, I found tons of tutorials online that guided me through themes and plugins. It was like opening a treasure chest of possibilities for customizing my site!
5 Best Domain Name Provider
| NO. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Namecheap | $8.88/year | Free WHOIS privacy, DNSSEC, 24/7 support | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | Domain.com | $9.99/year | Free SSL, 24/7 support, easy domain management | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | GoDaddy | $11.99/year | 24/7 support, domain auction, WHOIS privacy | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | Bluehost | $12.99/year | Free domain with hosting, 24/7 support, easy management | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | HostGator | $12.95/year | Free domain with hosting, 24/7 support, easy management | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
(iv) SSL Certificates
What is SSL?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, a security protocol that establishes an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser. This encryption ensures that any data transferred between the two remains private and secure. Although SSL has largely been replaced by Transport Layer Security (TLS), the term SSL is still widely used to refer to this technology.
What is an SSL certificate?
An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website's identity and enables an encrypted connection. This certificate contains important information, including the domain name, the certificate authority (CA) that issued it, and the public key used for encryption.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are several types of SSL certificates, each serving different needs:
- Domain Validated (DV) Certificates: These are the most basic type and provide minimal validation. They confirm that the applicant owns the domain.
- Organization Validated (OV) Certificates: These require more validation than DV certificates. The CA checks that the organization is legitimate before issuing the certificate.
- Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: These offer the highest level of security and require extensive verification of the organization’s identity. Websites with EV certificates display a green address bar in browsers, indicating higher trust.
- Wildcard Certificates: These allow you to secure a single domain and all its subdomains with one certificate.
- Multi-Domain Certificates: These can secure multiple domains under one certificate, which is useful for businesses with various websites.
- Unified Communications Certificates (UCC): Designed primarily for Microsoft Exchange and Office Communications environments, UCCs can secure multiple domains and host names.
When I was choosing an SSL certificate for my site, I opted for an OV certificate because I wanted to show visitors that my site was trustworthy without going through the extensive process required for an EV certificate.
How do SSL certificates work?
SSL certificates work through a process known as the SSL handshake. Here’s how it goes:
- A browser attempts to connect to a secured website.
- The browser requests that the web server identify itself.
- The web server sends its SSL certificate to the browser.
- The browser checks if it trusts the certificate by verifying its authenticity with the CA.
- If trusted, the browser generates a session key, encrypts it with the server's public key from the SSL certificate, and sends it back to the server.
- The server decrypts this session key using its private key.
- Now both parties can communicate securely using this session key.
I found this process fascinating when I first learned about it—it happens in mere milliseconds! But understanding it helped me appreciate why having an SSL certificate is vital for any website handling sensitive information.
Why do websites need an SSL certificate?
Websites need SSL certificates for several reasons:
- Security: They encrypt data transferred between users and servers, protecting sensitive information like personal details and credit card numbers.
- Trust: Users are more likely to trust websites with HTTPS in their URL and a padlock icon in their address bar.
- SEO Benefits: Search engines like Google give preference to HTTPS sites over HTTP ones, which can improve your search engine rankings.
When I switched my site from HTTP to HTTPS, I noticed an increase in traffic almost immediately! Users felt more secure browsing my content, which encouraged them to engage more with my posts.
What is a self-signed SSL certificate?
A self-signed SSL certificate is one that is signed by the individual or organization creating it rather than a trusted CA. While anyone can create one, browsers do not trust self-signed certificates by default because there’s no third-party verification of identity.
Is it possible to get a free SSL certificate?
Yes, it is possible to obtain free SSL certificates! Services like Let’s Encrypt provide free certificates that are easy to set up and renew automatically. Many hosting providers also offer free SSL certificates as part of their hosting packages.When I discovered Let’s Encrypt, I was thrilled! It made securing my site much easier without incurring additional costs.
How to Install SSL on Hosting
Installing an SSL certificate on your hosting account typically involves these steps:
- Purchase or obtain your SSL certificate: If you’re using Let’s Encrypt or another free provider, follow their instructions for obtaining your certificate.
- Access your hosting control panel: Log into your hosting account (like Bluehost or SiteGround).
- Locate the SSL section: This may be under security settings or similar categories.
- Upload your certificate files: If you purchased an SSL from a CA, you’ll need to upload your certificate files here.
- Activate the SSL: Once uploaded, make sure you activate it within your hosting panel settings.
- Test your installation: Use tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test to ensure everything is set up correctly.
I remember feeling accomplished after successfully installing my SSL certificate! It felt like I had taken a significant step toward making my website safer for visitors.
Best SSL Certificates Provider
| No. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Namecheap | $5.99/year | DV, OV, EV certificates, 24/7 support | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | Comodo SSL Store | $7.95/year | DV, EV, OV certificates, 24/7 support | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | SSLs.com | $36.75/year | DV, OV, EV certificates, fast turnaround | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | DigiCert | $269.73/year | OV, EV certificates, excellent support | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | Sectigo | $66/year | DV, OV, EV certificates, ideal for e-commerce | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
V. Web Hosting Performance Optimization
When it comes to web hosting, performance optimization is a game-changer. Trust me, I've been on both sides of the spectrum—having a sluggish site that made visitors bounce faster than a rubber ball and then finally getting my act together to optimize it.
So, let’s dive into what web hosting performance optimization really means and why it matters.
What is Web Hosting Optimization?
Web hosting optimization is all about making sure your website runs as smoothly and efficiently as possible. Think of it like tuning up a car before a long road trip. You wouldn’t want to hit the highway with an engine that sputters or tires that are low on air, right?
Similarly, optimizing your web hosting ensures that your site loads quickly, stays available, and provides a great user experience.
Key Factors in Optimization
- Server Location: The closer your server is to your audience, the faster your site will load for them. If your server is in the U.S. but most of your readers are in Europe, you’re in for some lag time.
- Resource Allocation: Different hosting plans offer different levels of resources like CPU and RAM. If you’re on a shared plan with limited resources, you might find your site slowing down during peak traffic times.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Utilizing a CDN can significantly boost your site’s speed by caching content across various locations worldwide, making it quicker for users to access your site.
- Caching: Implementing caching strategies can help reduce load times by storing copies of files so they don’t have to be fetched from the server every single time someone visits your site.
How Hosting Impacts Site Speed?
Let’s talk about speed because, honestly, it’s one of the most critical factors affecting user experience and SEO rankings. Google has been pretty clear about it—if your site takes longer than three seconds to load, you’re likely losing visitors.
In fact, research shows that 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than three seconds to load!When I finally switched to a better hosting provider that focused on speed optimizations—like SSD storage and LiteSpeed servers—I noticed a dramatic change.
My page load times went from over five seconds to under two seconds! This not only improved my bounce rate but also boosted my search engine rankings.
What is Hosting Uptime and Speed?
Uptime refers to the percentage of time your website is operational and accessible online. A high uptime percentage (like 99.9%) means your website is rarely down for maintenance or due to technical issues.
Conversely, downtime can lead to lost revenue and frustrated users.I once had a website that boasted 99% uptime but frequently went down for hours at a time due to server issues.
It was infuriating! Not only did I lose traffic during those downtimes, but my credibility took a hit too. Now, I always look for hosts that guarantee at least 99.9% uptime.
Why Uptime Matters
- User Trust: A reliable website builds trust with visitors; they’re more likely to return if they know they can access your content anytime.
- SEO Rankings: Search engines like Google favor websites with high uptime rates because they provide a better user experience.
What is 99.9% Uptime? and why it's Important?
So what does 99.9% uptime actually mean? It translates to about 8 hours of downtime per year—this includes scheduled maintenance and unexpected outages. While it sounds great on paper, it's essential to dig deeper into what this means for your website.
Imagine running an e-commerce store during the holiday season with only 99% uptime—that's nearly four days of potential downtime! For any business reliant on online sales or leads, every minute counts.
The Importance of High Uptime
- Financial Impact: Downtime can cost businesses thousands of dollars per minute in lost sales opportunities.
- Customer Experience: Users expect websites to be available 24/7; any downtime can lead them straight to competitors.
In my experience, finding a host that offers not just promises but actual performance metrics is crucial. Look for reviews and uptime guarantees backed by service level agreements (SLAs).
5 Best Hosting for Website Speed
| No. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hostinger | $2.99/month | SSD storage, Cache Manager, free CDN | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | SiteGround | $3.99/month | In-house performance tools, SSD storage | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | WP Engine | $20/month | Managed WordPress hosting, CDN, daily backups | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | A2 Hosting | $2.99/month | Turbo servers, SSD storage, free Cloudflare CDN | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | InMotion Hosting | $2.29/month | NVMe SSDs, UltraStack-powered hosting | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
Tools for Monitoring Uptime and Server Performance
Monitoring your website’s uptime and server performance is like having a security camera for your online presence. You want to know if something goes wrong before your visitors do. There are several tools out there that can help you keep an eye on things, and I’ve tried quite a few in my journey.
1. Pingdom
Pingdom is one of the first tools I ever used for monitoring my website's uptime. It’s user-friendly and provides real-time alerts when your site goes down. You can set up monitoring from various locations around the globe, which is super handy if you have an international audience. Plus, their performance reports help you understand load times and pinpoint areas needing improvement.
2. GTmetrix
GTmetrix is another gem. It not only checks your site’s speed but also gives you detailed insights into what might be slowing it down. I remember running my site through GTmetrix and realizing that my images were way too large—whoops! The recommendations it provides are actionable, making it easier to optimize your site effectively.
3. New Relic
If you’re looking for something a bit more advanced, New Relic is worth considering. It offers comprehensive monitoring that dives deep into server performance metrics. You can track everything from response times to error rates, which is invaluable when troubleshooting issues. It's like having a personal assistant that keeps you updated on how your server is performing.
4. UptimeRobot
UptimeRobot is a straightforward tool that does exactly what its name suggests: it monitors your uptime. The free version allows you to check your site every five minutes, which is pretty decent for most small websites. I’ve found it particularly useful for getting instant notifications via email or SMS if my site goes down.
5. Site24x7
Site24x7 offers a robust suite of monitoring tools that cover everything from uptime checks to server health monitoring. It’s great for those who want an all-in-one solution. The dashboard is intuitive, making it easy to visualize performance metrics at a glance.Having these tools at your disposal can save you from potential disasters. I learned this the hard way when I didn’t monitor my site closely enough and missed out on important traffic because of unexpected downtime.
How to Optimize Hosting Performance?
Now that we’ve got monitoring covered, let’s talk about how to actually optimize your hosting performance. This is where the rubber meets the road! Here are some practical tips based on my experiences:
1. Upgrade Your Hosting Plan
Sometimes, the best way to improve performance is simply to upgrade your hosting plan. If you're on shared hosting and find that your site slows down during pdedicated hostingeak traffic times, consider switching to VPS or . When I made this switch, my site’s speed improved significantly because I had more resources at my disposal.
2. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN distributes your website's content across multiple servers worldwide, ensuring that users access data from the nearest location. This dramatically reduces load times for visitors who are far from your main server. I implemented a CDN after noticing slow load times for international visitors—what a difference it made!
3. Optimize Images
Images can be one of the biggest culprits in slowing down a website. Always compress images before uploading them using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim. I used to upload high-resolution images without thinking twice until I realized they were dragging my site down.
4. Enable GZIP Compression
Enabling GZIP compression reduces the size of files sent from your server to increase transfer speeds. Most hosting providers allow this feature; just check your control panel settings or ask support if you're unsure how to enable it.
5. Minify CSS and JavaScript Files
Minifying CSS and JavaScript files involves removing unnecessary characters (like spaces and comments) from code without changing its functionality. This reduces file sizes and speeds up load times significantly. There are various plugins available for WordPress that can handle minification automatically, which makes life so much easier!
6. Implement Caching
Caching stores parts of your website so they don’t have to be fetched from the server every time someone visits your page—this can drastically improve load times! For WordPress sites, plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Super Cache work wonders.
7. Choose the Right PHP Version
Using an outdated PHP version can slow down your site considerably. Upgrading to a faster version (like PHP 7 or newer) can enhance performance by up to 30%. Just make sure to test everything after upgrading since some older applications might not be compatible.
8. Limit Plugins
While plugins can add fantastic functionality to your website, too many can lead to bloat and slow loading times. Regularly review the plugins you have installed and disable any that aren’t essential—this was a tough lesson learned after realizing some plugins were causing conflicts and slowing things down.
9. Regular Audits
Finally, make website speed testing part of your routine! After updates or major changes, run tests using tools like GTmetrix or Pingdom to ensure everything is still running smoothly.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll not only enhance user experience but also improve search engine rankings—everyone wins! Remember, optimizing hosting performance isn’t just about speed; it’s about creating a seamless experience for everyone who visits your site.
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Understanding Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) is essential for anyone looking to optimize their website’s performance. CDNs are a powerful tool that can significantly enhance load times, improve reliability, and reduce costs.
Let’s break down what a CDN is, how it works, and the benefits it brings to your website.
What is CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a system of distributed servers that deliver web content to users based on their geographic location. Essentially, a CDN caches content from your website—like images, videos, and scripts—on multiple servers around the world.
This means that when someone visits your site, they can access it from the nearest server, reducing latency and improving load times.
For example, if a user in Australia visits a website hosted in the United States, without a CDN, their request would have to travel all the way to the U.S. and back. But with a CDN, they would be served from a nearby server located in Australia or Asia, making the process much faster.
Is a CDN the same as a web host?
Nope! A CDN is not the same as a web host. Traditional web hosting involves storing your website files on a single server or a group of servers in one location. When users access your site, they retrieve data directly from that server.
In contrast, a CDN uses multiple servers spread across various locations to deliver content more efficiently.
To illustrate this difference: think of web hosting as having your store located in one city. If customers come from far away, they have to travel long distances to get to you.
A CDN is like opening multiple branches of your store in different cities—customers can visit the nearest one and get what they need quickly.
How does a CDN work?
A CDN works by caching content on edge servers strategically placed around the globe. Here’s how it typically operates:
- Caching: When you upload content to your website, the CDN creates copies of that content and stores it on its edge servers.
- User Request: When someone visits your site, their request is routed to the nearest edge server rather than your main server.
- Content Delivery: The edge server delivers the cached content directly to the user, which reduces latency because the data doesn’t have to travel as far.
For instance, if you’re using a service like Cloudflare or Amazon CloudFront, they automatically cache your static assets (like images and CSS files) on their network of servers.
What are the benefits of using a CDN?
Using a CDN comes with several advantages:
- Improved Load Times: By serving content from locations closer to users, CDNs significantly reduce load times.
- Increased Reliability: CDNs can handle high traffic loads better than traditional web hosting because they distribute requests across multiple servers.
- Scalability: During traffic spikes (like holiday sales), CDNs can absorb extra load without crashing.
- Enhanced Security: Many CDNs offer security features like DDoS protection and secure token authentication.
For example, major companies like Netflix use CDNs to ensure their streaming service remains fast and reliable for millions of users worldwide.
How does a CDN improve website load times?
Latency refers to the delay before data begins to transfer after a request is made. A CDN minimizes latency by caching content close to users’ locations. When users request data from your site:
- Instead of reaching out to your origin server (which might be far away), they connect with an edge server nearby.
- This drastically reduces the time it takes for data packets to travel back and forth.
According to KeyCDN's tests, implementing their CDN reduced load times from 612 ms down to 378 ms—an impressive 38% improvement! This means faster loading pages and happier visitors.
How does a CDN keep a website always online?
CDNs enhance uptime by distributing traffic across multiple servers. If one server goes down or experiences issues:
- Other servers in different locations can still serve cached content.
- This redundancy ensures that even if one part of the network fails, users can still access your website from another edge server.
This was evident during high-profile events like Black Friday sales when websites experience massive traffic surges; many rely on CDNs to maintain availability without crashing.
How does a CDN protect data?
Data protection is another critical benefit of using a CDN. Here’s how they help:
- DDoS Mitigation: CDNs are designed to absorb DDoS attacks by distributing incoming traffic across their network instead of overwhelming your origin server.
- Secure Connections: Many CDNs offer SSL certificates and secure connections (HTTPS), ensuring that data transmitted between users and servers is encrypted.
For instance, Akamai’s CDN has been known for its robust security features that protect against various types of attacks while maintaining performance.
How does a CDN reduce bandwidth costs?
CDNs can help lower bandwidth costs through caching:
- By serving cached content from edge servers instead of pulling it from the origin server each time, you reduce the amount of data transferred from your main hosting provider.
- This not only speeds up delivery but also decreases bandwidth usage on your main server—saving you money in hosting fees.
For example, KeyCDN reported that one client saw their bandwidth usage drop significantly after implementing their service—indicating how effective CDNs can be at managing costs while improving performance.
Which CDN is best for a website?
Choosing the best CDN depends on several factors like budget, specific needs, and target audience location. Here are some popular options:
- Cloudflare: Great for small businesses due to its free tier and robust security features.
- Amazon CloudFront: Ideal for larger enterprises needing extensive customization and integration with other AWS services.
- Akamai: Known for its comprehensive security features and global reach—often used by big brands like Apple and Microsoft.
- Fastly: Excellent for real-time analytics and dynamic content delivery; favored by media companies like The New York Times.
Top 5 CDN Providers
| No. | Provider | Price | Features | Rating | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cloudflare | Free plan available; paid plans start at $20/month | Global network, DDoS protection, free SSL | 4.8/5 | Visit Website |
| 2 | KeyCDN | $0.04 per GB for the first 10 TB | Real-time analytics, HTTP/2 support, free SSL | 4.7/5 | Visit Website |
| 3 | Google Cloud CDN | $0.08 per GiB in North America and Europe | Integration with Google Cloud, global network | 4.6/5 | Visit Website |
| 4 | Amazon CloudFront | $0.085 per GB | Integration with AWS, global network, DDoS protection | 4.5/5 | Visit Website |
| 5 | Microsoft Azure CDN | $0.087 per GB | Integration with Azure, global network, flexible pricing | 4.4/5 | Visit Website |
Caching and Compression
Caching and compression are two essential techniques for improving website performance. They help reduce load times, enhance user experience, and optimize resource usage.
Let’s explore what caching and compression are, how they work, their differences, and how they contribute to better website performance.
What is Caching?
Caching is the process of storing copies of files or data in a temporary storage area, so they can be accessed more quickly in the future. When a user visits a website, certain elements like images, stylesheets, and scripts are retrieved from the server.
Caching allows these elements to be saved locally on the user's device (browser caching) or on the server (server caching) for faster retrieval on subsequent visits.
Types of Caching
- Browser Caching: This type stores web files in the user's browser. When a user revisits a site, their browser can load cached files instead of downloading them again from the server. For example, when you visit YouTube for the first time, it takes longer to load because your browser downloads all the necessary assets. However, on subsequent visits, your browser retrieves these assets from its cache, speeding up load times significantly.
- Server Caching: Server-side caching stores web files and data on the server
itself. There are two primary types:
- Full-Page Caching: This involves storing entire HTML pages generated by the server. For instance, if a user requests a frequently visited page, the server can deliver the cached version instead of regenerating it each time.
- Fragment Caching: This focuses on caching specific components of a page rather than the entire page. For example, a site might cache a sidebar that contains frequently updated links while allowing other parts of the page to change dynamically.
How does cache work?
When a user requests a webpage, the server checks if there’s a cached version available. If it exists, the server delivers this cached version instead of processing the request from scratch. This reduces server load and speeds up response times.
HTTP headers like Cache-Control and Expires dictate how long content should be cached before it needs to be revalidated or fetched anew.
For example, if an e-commerce site has a popular product page that rarely changes, full-page caching can serve that page quickly to users without needing to regenerate it from scratch each time someone visits.
What is Compression?
Compression is the process of reducing the size of files sent over the internet without losing essential data or quality.
By compressing files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript before they are sent to users’ browsers, websites can decrease loading times and improve performance.
How does compression work?
Compression works by using algorithms to reduce file sizes. When a user requests a webpage:
- The server compresses files using methods like Gzip or Brotli.
- The compressed files are sent to the user's browser.
- The browser decompresses these files before rendering them.
For instance, when you visit a news website that uses Gzip compression, large HTML files can be reduced significantly—sometimes by 70% or more—resulting in faster loading times.
What is the difference between caching and compression?
While both caching and compression aim to improve website performance, they operate differently:
- Caching stores copies of data for quick retrieval on subsequent requests.
- Compression reduces file sizes during transmission to speed up loading times.
In essence, caching helps avoid repeated data generation or retrieval from servers while compression minimizes bandwidth usage during data transfer.
How does caching and compression improve website performance?
Both caching and compression contribute significantly to enhanced website performance in various ways:
- Reduced Load Times: By serving cached content directly from local storage (in browsers) or memory (on servers), websites can load much faster compared to fetching data anew each time.
- Lower Server Load: Caching reduces the number of requests made to servers by serving stored copies instead of generating new content for every request. This is particularly beneficial during high-traffic events like Black Friday sales when many users access the same pages simultaneously.
- Decreased Bandwidth Costs: Compression lowers file sizes during transfer, which means less data needs to be sent over the network. This not only speeds up loading times but also reduces bandwidth costs for web hosts.
- Improved User Experience: Faster loading times lead to better user satisfaction and lower bounce rates. According to Google’s research, even a one-second delay in load time can lead to significant drops in conversions.
For example, major websites like Amazon use both caching and compression techniques extensively. They implement aggressive caching strategies for product pages that don’t change often while also compressing images and scripts to ensure quick delivery across their global audience.
How to Enable Caching in Hosting?
Enabling caching on your hosting service can vary depending on the provider. For example, if you’re usingBluehost, they offer built-in caching options that can be easily activated through their dashboard.
- Log into Your Bluehost Account: Start by accessing your Bluehost control panel.
- Navigate to Performance Settings: Look for the "Performance" tab in the main menu. This section contains various optimization features.
- Enable Caching: In the Performance section, you will find an option for "Caching." Simply toggle it on to activate caching for your site. Bluehost typically uses a system called LiteSpeed Cache, which is highly effective for speeding up WordPress sites.
- Configure Additional Settings: After enabling caching, you may want to explore additional settings such as cache expiration times or specific cache rules for different pages.
- Clear Cache: Whenever you make updates to your site, remember to clear the cache from the same settings page to ensure visitors see the latest content.
By following these steps, you can leverage Bluehost’s built-in caching features to improve your website’s performance significantly.
How to Optimize Caching and Compression?
Optimizing caching and compression involves several strategies that can enhance your website's speed and efficiency:
- Set Appropriate Cache Expiration Times: Determine how long content should be cached based on how frequently it changes. Static content can be cached longer than dynamic content.
- Use Browser Caching: Configure browser caching rules so that returning visitors can load cached files instead of fetching them from the server again. This is especially beneficial for images and stylesheets.
- Leverage Server-Side Caching: Utilize server-side caching solutions like Varnish or Redis if your hosting provider supports them. These technologies can significantly speed up data retrieval.
- Implement Gzip Compression: Ensure that Gzip compression is enabled on your server to reduce file sizes during transfer, which speeds up load times.
- Minify Files: Minification involves removing unnecessary characters from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files without affecting functionality. This reduces file sizes and improves loading speed.
- Regularly Monitor Performance: Use tools like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights to analyze your site’s performance regularly and identify areas for improvement.
By applying these optimization techniques, you can ensure that both caching and compression work effectively together to enhance user experience.
Best Caching and Compression Tools
There are several excellent tools available for managing caching and compression:
- Cloudflare: This popular CDN service not only provides caching but also offers security features like DDoS protection and SSL support. Cloudflare's caching rules can be customized based on your needs.
- Varnish Cache: A powerful HTTP accelerator designed for high-traffic websites, Varnish caches web pages in memory, allowing for extremely fast retrieval times.
- Redis: Often used in conjunction with other caching systems, Redis is an in-memory data structure store that can be used as a database or cache to improve performance.
- Gzip Compression Tools: Most web servers support Gzip compression natively, but tools like Gzip Ninja can help configure it properly if needed.
- Image Optimization Tools: While not directly related to caching, tools like ShortPixel or Imagify compress images effectively without losing quality, which complements caching strategies by reducing load times further.
Best Caching and Compression Plugins
For WordPress users, several plugins are available that simplify the process of implementing caching and compression:
- WP Rocket: Widely regarded as one of the best caching plugins, WP Rocket offers features like page caching, cache preloading, Gzip compression, and browser caching—all with a user-friendly interface that requires minimal setup.
- W3 Total Cache: This comprehensive plugin provides extensive options for optimizing site performance through various types of caching (page, database, object) and integrates well with CDNs.
- WP Super Cache: A straightforward plugin that generates static HTML files from your dynamic WordPress site, making it easier for servers to serve content quickly without heavy processing.
- LiteSpeed Cache: Ideal for users on LiteSpeed servers, this plugin offers server-level caching along with image optimization features and support for various web optimization techniques.
- Autoptimize: While primarily focused on minification and concatenation of scripts and stylesheets, Autoptimize works well alongside other caching plugins to enhance overall performance by optimizing file delivery.
- Sucuri Security: Although primarily a security plugin, Sucuri includes built-in caching capabilities that help improve site speed while providing robust security features against attacks.
Scalability and Resource Management
Scalability and resource management are critical components of web hosting that ensure your website can handle increasing traffic and demands without compromising performance. Understanding these concepts can help you make informed decisions about your hosting solutions as your online presence grows.
Let’s break down what web hosting scalability is, how to scale your hosting as traffic grows, and the importance of resource management.
What is Web Hosting Scalability?
Web hosting scalability refers to the ability of a hosting environment to accommodate increased traffic and resource demands without significant downtime or performance degradation. It allows websites to adapt seamlessly as user demand fluctuates.
Essentially, a scalable hosting solution can grow alongside your business, ensuring that you have the necessary resources to handle spikes in traffic or data usage.For instance, consider an e-commerce website that experiences a surge in visitors during holiday sales.
A scalable hosting solution ensures that the site remains accessible and responsive during peak periods, preventing slow load times or downtime that could result in lost sales.
How to Scale Your Hosting as Traffic Grows?
Scaling your hosting involves several strategies to manage increased traffic effectively:
- Monitor Traffic Patterns: Use analytics tools to track visitor behavior and identify peak traffic times. This data helps you anticipate when you might need additional resources.
- Choose the Right Hosting Plan: Start with a plan that offers scalability options. For example, many providers offer shared hosting plans that can be upgraded to VPS or dedicated servers as your needs grow.
- Implement Load Balancing: Distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers can help manage high volumes of requests without overloading a single server.
- Utilize Cloud Hosting: Cloud hosting solutions allow you to draw resources from multiple servers, making it easier to scale up or down based on current demand.
- Auto-Scaling Solutions: Some hosting providers offer auto-scaling features that automatically adjust resources based on real-time traffic demands, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention.
Auto-Scaling Hosting Solutions
Auto-scaling is a feature offered by many cloud hosting providers that automatically adjusts server resources based on current traffic levels. This means that during periods of high demand, additional resources are allocated automatically, and when traffic decreases, those resources are scaled back down.
For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides an auto-scaling feature that allows businesses to set rules for scaling their resources up or down based on specific metrics such as CPU usage or network traffic.
This ensures that websites remain responsive during sudden spikes in traffic while also optimizing costs by reducing unnecessary resource allocation during quieter periods.
Resource Management in Hosting
Effective resource management is crucial for maintaining optimal website performance. It involves monitoring and allocating server resources—such as CPU, RAM, and bandwidth—based on current needs and anticipated growth.
- Analyze Resource Usage: Regularly review your site’s resource consumption using analytics tools to understand how much CPU and memory your site requires under different conditions.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Utilize tools provided by your hosting provider to allocate resources dynamically based on current demand. This ensures that users receive the necessary performance without overprovisioning.
- Plan for Growth: Anticipate future needs based on projected growth and marketing campaigns. This proactive approach helps avoid service interruptions when traffic increases unexpectedly.
- Implement Caching Strategies: Caching can significantly reduce server load by storing frequently accessed data temporarily, allowing faster retrieval for users without taxing server resources heavily.
Upgrading from Shared to VPS or Dedicated Servers
As your website grows, you may find that shared hosting no longer meets your needs due to limited resources and potential performance issues during peak traffic times. Upgrading to Virtual Private Servers (VPS) or dedicated servers can provide the necessary power and flexibility for growing websites.
VPS Hosting
VPS hosting offers a middle ground between shared and dedicated hosting. With VPS, you still share a physical server with other users, but you have dedicated virtual resources allocated specifically for your site.
This means better performance, more control over server configurations, and the ability to scale resources easily as needed.
For example, a small business website may start with shared hosting but switch to VPS as their online store gains traction and experiences increased traffic during promotions or holiday sales.
Dedicated Servers
Dedicated servers provide the highest level of performance and control since you have an entire server exclusively for your website. This option is ideal for large businesses or high-traffic sites that require substantial resources and customization capabilities.
For instance, popular streaming services like Netflix rely on dedicated servers to manage vast amounts of data transfer while ensuring fast load times for viewers around the world.
VI. Security and Backups in Web Hosting
With the increasing number of cyber threats, ensuring that your web hosting environment is secure and that you have reliable backup solutions in place is essential.
Let’s explore the key aspects of web hosting security features, malware protection, firewalls, the importance of regular security audits, and two-factor authentication.
Web Hosting Security Features:
Web hosting security features are essential for protecting your website from various threats. Here are some of the best security features to consider when selecting a hosting provider:
- Data Backups: Regular backups are crucial for data recovery in case of a breach or server failure. Many hosting providers offer automated backup solutions, allowing you to restore your site quickly if needed. For instance, DigitalOcean provides automatic backups for managed databases, ensuring your data is safe without manual intervention.
- Malware Detection and Removal: Hosting services should include tools for scanning and eliminating malware. This feature helps identify malicious software before it can cause damage. For example, Hostinger integrates malware scanning within its control panel to automatically check for harmful files.
- SSL Certificates: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates encrypt data transmitted between users and your website, protecting sensitive information like login credentials and payment details. Many hosts, including Hostinger, offer free SSL certificates with their plans.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF): A WAF monitors and filters incoming traffic to block malicious requests before they reach your server. This layer of protection can prevent common attacks such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Services like Sucuri provide robust WAF solutions that also include caching features to enhance performance.
- DDoS Protection: Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm your server with traffic, causing downtime. Effective DDoS protection helps mitigate these attacks by filtering out malicious traffic before it reaches your site. Hosting providers like Cloudflare offer advanced DDoS protection as part of their services.
Best Security Features for Hosting
When evaluating web hosting providers, look for the following essential security features:
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping software up-to-date is vital for patching vulnerabilities. Many hosts automatically apply updates to their software stack.
- Network Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of network traffic helps identify suspicious activities early on. This proactive approach can prevent potential breaches.
- Strong Password Policies: Encouraging strong password management practices can significantly enhance account security.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implementing 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a second method, such as a mobile app or SMS.
Web Hosting Malware Protection
Web hosting malware protection involves various strategies and tools designed to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software from your server. Effective malware protection includes:
- Automated Scanning: Regularly scheduled scans help identify vulnerabilities and malware infections before they escalate into serious issues.
- Real-time Protection: Some hosting providers offer real-time monitoring that alerts you to potential threats as they occur.
- Malware Removal Services: In the event of an infection, many hosts provide services to clean up infected files and restore your site to a secure state.
For instance, CloudPanel emphasizes the importance of having built-in malware detection tools as part of its hosting solution.
Hosting Firewalls and DDoS Protection
Firewalls act as a barrier between your web server and potential threats from the internet. They filter incoming traffic based on predetermined security rules, blocking unauthorized access attempts.
DDoS Protection
DDoS protection is crucial for maintaining uptime during an attack. Effective DDoS mitigation strategies include:
- Traffic Filtering: Identifying and blocking malicious traffic while allowing legitimate requests through.
- Rate Limiting: Limiting the number of requests from a single IP address can help mitigate the effects of an attack.
- Traffic Diversion: Some services redirect traffic through scrubbing centers where malicious traffic is filtered out before reaching your server.
For example, DigitalOcean includes DDoS protection in its cloud infrastructure offerings to ensure that websites remain accessible even during high-volume attacks.
Importance of Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits is vital for identifying vulnerabilities within your web hosting environment. These audits help ensure that all components—software, configurations, and policies—are up-to-date and secure.
Benefits of Security Audits:
- Identify Weaknesses: Regular assessments can uncover potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries require regular audits to comply with regulations regarding data protection and privacy.
- Improved Security Posture: Audits help organizations develop better security practices based on identified weaknesses.
Two-Factor Authentication and Account Security
Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances account security by requiring two forms of verification before granting access. This additional layer makes it significantly harder for unauthorized users to gain access even if they have stolen login credentials.
How 2FA Works:
- Primary Authentication: Users enter their username and password as usual.
- Secondary Verification: After entering credentials, users must provide a second form of identification—typically a code sent via SMS or generated by an authentication app like Google Authenticator.
Implementing 2FA is a straightforward yet effective way to bolster account security across various platforms, including web hosting accounts.
Backups
Understanding the various types of backups, their importance, and how to implement them effectively can save you from potential disasters.
Let’s dive into what web hosting backups are, their importance, the differences between automated and manual backups, how to back up your website, and the best backup solutions available.
What is Web Hosting Backups?
Web hosting backups refer to the process of creating copies of your website's data, including files, databases, and configurations. These backups serve as a safety net, allowing you to restore your website to a previous state in case of data loss due to server failures, accidental deletions, malware attacks, or other unforeseen events.
For instance, if a website experiences a catastrophic server crash or a cyberattack that compromises its data, having recent backups can mean the difference between a quick recovery and significant downtime.
Importance of Backups for Website Data
The importance of backups cannot be overstated. Here are several key reasons why maintaining regular backups is essential:
- Data Recovery: Backups allow you to restore lost or corrupted data quickly. In the event of an attack or failure, you can revert to the last known good configuration.
- Protection Against Human Error: Accidental deletions or changes are common. Regular backups ensure that even if a mistake occurs, you can recover your work without significant loss.
- Mitigation of Cyber Threats: With the rise in cyberattacks, having backups helps safeguard against ransomware and other malicious threats that could compromise your website’s integrity.
- Business Continuity: For businesses that rely on their online presence, maintaining regular backups is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operations.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that you have reliable backups can alleviate stress and allow you to focus on growing your business rather than worrying about data loss.
Automated vs. Manual Backups
When it comes to backing up your website, you generally have two options: automated and manual backups. Each method has its pros and cons.
Automated Backups
Automated backups run on a set schedule without requiring human intervention. These systems typically create incremental backups, meaning only changes made since the last backup are saved.
This method is efficient and ensures that your data is consistently backed up without relying on memory or manual effort.
For example, many hosting providers like WP Umbrella offer automated backup solutions that allow users to schedule backups daily or weekly while storing them for an extended period (up to 50 days). This approach minimizes the risk of human error and ensures that data is always up-to-date.
Manual Backups
Manual backups require users to initiate the backup process themselves. While this method offers more control over what gets backed up and when it happens, it also demands more time and effort.
Manual backups can be resource-intensive and are often limited in frequency due to storage constraints.For instance, some services limit users to only three manual backups per month due to the heavy resource usage involved.
This approach might be suitable for smaller websites or specific situations where users want to back up critical changes before major updates.
How to Backup Website on Hosting
Backing up your website can vary depending on your hosting provider, but here i will show you how to back up your website on Bluehost which is straightforward thanks to their user-friendly interface. Here’s how you can do it:
- Log into Your Bluehost Account: Start by accessing your Bluehost control panel.
- Navigate to the Backup Section: Look for the "Backup" option in the "Advanced" tab within your account dashboard.
- Choose Backup Options: Bluehost offers options for both manual and
automatic
backups. You can select what type of backup you want:
- For manual backups, choose "Backup Now" to create an immediate copy of your site.
- For automated backups, you can set up a schedule based on your preferences (daily, weekly).
- Download Your Backup (Optional): If you want an additional copy stored locally on your computer, you can download the backup files directly from the control panel.
- Restore from Backup (if needed): If something goes wrong and you need to restore your site, simply navigate back to the backup section and select the restore option for the desired backup date.
By following these steps on Bluehost, you can ensure that your website is backed up regularly and efficiently.
Best Backup Solutions for Hosting
When selecting a backup solution for web hosting, consider these options:
- BackupBuddy: A popular WordPress plugin that allows users to schedule automatic backups and store them remotely (e.g., Dropbox, Amazon S3). It also offers easy restoration features.
- UpdraftPlus: Another excellent WordPress plugin that provides automated backup scheduling with options for cloud storage integration. Its user-friendly interface makes it easy to manage backups.
- Acronis Cyber Backup: A comprehensive solution suitable for businesses needing robust protection against data loss with features like continuous data protection and ransomware protection.
- VaultPress (Jetpack Backup): Developed by Automattic (the company behind WordPress), VaultPress offers real-time backup solutions with easy restoration options tailored specifically for WordPress sites.
- cPanel Backups: If your hosting provider uses cPanel (like many do), it often includes built-in backup features that allow users to create full or partial backups easily through their dashboard.
- CodeGuard: A cloud-based backup solution that provides automatic daily backups along with monitoring features that alert users about changes made to their websites.
Disaster Recovery
What is Disaster Recovery in Hosting?
Disaster recovery in hosting refers to the strategies and processes implemented to protect and restore a website’s functionality after a disruptive event. This can include anything from hardware failures and cyberattacks to natural disasters like floods or earthquakes.
The goal of a disaster recovery plan is to minimize downtime and data loss, ensuring that the website can return to normal operations as quickly as possible.
For instance, if a server crashes due to hardware failure, a well-structured disaster recovery plan would allow the hosting provider to switch operations to a backup server seamlessly, minimizing disruption for users.
How to Restore Website Backup?
Restoring a website backup is a crucial step in disaster recovery. Here’s a general process for restoring backups, using common practices that many hosting providers follow:
- Access Backup Storage: Log into your hosting control panel where your backups are stored. This could be an integrated backup solution provided by your host or an external storage service.
- Select the Backup: Identify the most recent backup that you want to restore. Ensure it’s from a time before the issue occurred (for example, before a cyberattack or data corruption).
- Initiate Restoration: Most hosting providers will have a straightforward restoration option. For example, in Bluehost, you would navigate to the backup section and select "Restore" next to the desired backup date.
- Follow Prompts: Complete any prompts or confirmations required by your hosting provider. This may include selecting specific files or databases if you’re not restoring the entire site.
- Verify Restoration: Once the restoration process is complete, check your website thoroughly to ensure everything is functioning as expected and all data has been restored correctly.
- Update Security Measures: After restoring your site, it’s crucial to review and update your security measures to prevent future incidents.
Disaster Recovery Plans for Hosting
A disaster recovery plan outlines the steps necessary to recover from various types of incidents that could affect your website's availability. Here are key components to consider when developing a disaster recovery plan:
1. Assess Potential Threats
Identify potential threats that could impact your website’s operations. Common threats include:
- Server Crashes: Hardware or software failures that render your server inoperable.
- Cybersecurity Breaches: Attacks from hackers that compromise site integrity or steal sensitive data.
- Natural Disasters: Events like floods or earthquakes that may disrupt physical infrastructure.
- Human Errors: Mistakes made during updates or maintenance that can lead to outages.
2. Set Recovery Objectives
Establish clear Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO):
- RTO defines how quickly you need your website back online after an incident.
- RPO determines how much data loss is acceptable (i.e., how often backups should be taken).
3. Backup Your Website Regularly
Implement regular backup schedules for both files and databases. Many hosting providers offer automated backup solutions that can run daily or weekly, ensuring you always have recent copies of your data.
4. Choose the Right Hosting Provider
Select a hosting provider that offers robust disaster recovery features, including redundancy in their infrastructure (like multiple data centers) and automated failover systems for minimal downtime during hardware failures.
5. Develop a Recovery Strategy
Create a detailed strategy outlining specific actions to take during different types of disasters:
- Communication Plan: Establish who needs to be notified during an incident.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assign tasks to team members involved in the recovery process.
- Testing Procedures: Regularly test your disaster recovery plan through simulations to identify weaknesses.
6. Document Everything
Maintain comprehensive documentation of your disaster recovery plan, including contact information for key personnel, step-by-step instructions for restoring services, and any necessary credentials.By following these guidelines, businesses can develop effective disaster recovery plans tailored to their unique needs, ensuring they are prepared for unexpected events.
VII. How to Set Up Web Hosting
Creating a website may seem daunting at first, but breaking it down into simple steps can make the process much more manageable.
Here’s a straightforward guide to help you host your website effectively, from deciding on the type of website you want to creating or uploading your content.
5 Simple Steps to Host a Website
1. Decide on Your Website Type
The first step in hosting a website is determining what type of website you want to create. This decision will influence everything from design to functionality. Here are some common types of websites:
- Business Websites: These sites provide information about your products or services and often include contact details and customer testimonials.
- E-commerce Websites: Designed for selling products online, these sites require features like shopping carts and payment gateways.
- Blogging Websites: Focused on sharing articles and personal insights, blogs are great for engaging with an audience.
- Portfolio Websites: Ideal for showcasing work, especially for creatives like photographers or designers.
- Informational Websites: These sites aim to provide detailed information about a particular subject or service.
Understanding your goals and target audience will help you choose the right type of website that aligns with your business objectives.
2. Choose a Web Hosting Provider
Once you know the type of website you want, the next step is selecting a web hosting provider. Look for a provider that offers reliable uptime, good customer support, and features that match your needs.
Understanding your goals and target audience will help you choose the right type of website that aligns with your business objectives.
Pro Tip: If you’re just starting out, shared hosting plans from Bluehost or Hostinger are often sufficient and budget-friendly. They also provide features like one-click WordPress installation, making it easy to set up your site.
4. Get and Register a Unique Domain Name for Your Website
Your domain name is your website's address on the internet, so choose something memorable and relevant to your brand.
Pro Tip: Both Bluehost and Hostinger offer free domain registration for the first year when you purchase their hosting plans. This can save you money while establishing your online presence.
5. Create or Upload Your Website
Once you have your domain name and hosting plan set up, it’s time to create or upload your website:
- Using a Website Builder: Many hosting providers offer built-in website builders that allow you to create your site using templates without needing coding skills.
- Uploading Your Site: If you've already built your site using software like WordPress or another CMS (Content Management System), you can upload it via FTP (File Transfer Protocol) using tools like FileZilla.
After uploading or building your site, ensure everything looks good and functions properly before launching it to the public.
Installing a Content Management System (CMS)
Installing a Content Management System (CMS) is a crucial step in building a website, as it allows you to manage your content easily without needing extensive coding knowledge.
Let's delve into what a CMS is, how to install WordPress on your hosting, the differences between one-click installations and manual setups, and explore some of the best CMS platforms available.
What is CMS?
A Content Management System (CMS) is software that enables users to create, edit, manage, and publish digital content without requiring deep technical skills. With a CMS, you can build and maintain websites through a user-friendly interface that abstracts the complexities of coding.A CMS typically consists of two main components:
- Content Management Application (CMA): This is the front-end interface where users create and manage content.
- Content Delivery Application (CDA): This back-end service handles the delivery of content to users.
For example, popular CMS platforms like WordPress allow users to easily add blog posts, images, and pages without needing to write HTML or CSS from scratch. This accessibility makes it easier for individuals and businesses to maintain their online presence.
How to Install WordPress on Hosting?
Installing WordPress on your hosting account is a straightforward process. Here’s how you can do it:
- Log into Your Hosting Account: Access your hosting provider’s dashboard (e.g., Bluehost or Hostinger).
- Navigate to the WordPress Installer: Most hosting providers have a dedicated section for installing WordPress. Look for options like "WordPress" or "Website" in your control panel.
- Select One-Click Installation: Many hosts offer a one-click installation feature for WordPress. Click on this option, and follow the prompts to choose your domain name and set up your admin account.
- Complete the Installation: After filling out the necessary details, click “Install.” The process typically takes just a few minutes.
- Access Your WordPress Dashboard: Once installed, you can access your
WordPress
dashboard by going to
yourdomain.com/wp-admin, where you can start customizing your site.
One-Click Installations vs. Manual Setups
One-Click Installations
One-click installations are automated processes provided by many hosting companies that allow users to install applications like WordPress with minimal effort. Users simply select their desired application and follow prompts to complete the installation.
Pros:
- Ease of Use: Ideal for beginners who may not be comfortable with technical setups.
- Time-Saving: Installation is quick and often completed in just a few minutes.
Manual Setups
Manual installations involve downloading the CMS files from the official website, uploading them to your server via FTP (File Transfer Protocol), and configuring settings through a database setup process.
Pros:
- Greater Control: Offers more customization options during installation.
- Learning Opportunity: Provides insight into how web applications are structured and function.
However, manual setups can be more complex and time-consuming, making them less appealing for those new to web development.
Best CMS Platforms
There are several excellent CMS platforms available today, each with unique features suited for different needs:
- WordPress: The most popular CMS globally, powering over 40% of all websites. It offers extensive themes and plugins for customization and is ideal for blogs, e-commerce sites, and portfolios.
- Joomla: A flexible platform that balances ease of use with advanced capabilities. It's suitable for complex websites but may have a steeper learning curve than WordPress.
- Drupal: Known for its robust security features and flexibility, Drupal is ideal for larger organizations or sites requiring complex data organization but requires more technical expertise.
- Wix: A cloud-based website builder that allows users to create sites using drag-and-drop functionality without needing coding skills. It’s great for small businesses or personal projects.
- Squarespace: Offers beautiful design templates and an intuitive interface ideal for creatives looking to showcase their work online without technical hassles.
- Shopify: Specifically designed for e-commerce websites,Shopify provides all the tools needed to create an online store quickly and efficiently.
By choosing the right CMS platform based on your needs—whether it's blogging, e-commerce, or portfolio management—you can streamline your website management process while focusing on creating engaging content for your audience.
Migrating Your Website to a New Host
Whether you're switching for better performance, customer support, or pricing, understanding how to migrate effectively is crucial.
Here’s a comprehensive guide on migrating your website, including common reasons for switching hosting providers and a detailed step-by-step process.
Common Reasons for Switching Hosting Providers
There are several reasons why you might consider migrating your website to a new hosting provider:
- Performance Issues: If your current host is slow or frequently experiences downtime, it can negatively impact user experience and SEO rankings. A faster host can improve load times and overall site performance.
- Customer Support: Poor customer support can lead to frustration, especially during critical issues. Switching to a provider known for responsive and helpful support can save you time and stress.
- Cost: You may find more affordable options that offer better features or resources. Many providers have promotional rates that can significantly reduce your hosting costs.
- Scalability: As your website grows, you may need more resources than your current host can provide. A new provider might offer better scalability options to accommodate future growth.
- Security Features: Enhanced security features such as automated backups, SSL certificates, and DDoS protection may be available with a new host, providing better protection for your site.
How to migrate a website from one hosting to another?
Migrating your website involves several steps to ensure that the transition is seamless and that no data is lost in the process. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Step 1: Choose Your New Hosting Provider and Plan
Select a new hosting provider that meets your needs based on performance, support, scalability, and cost. For example, Bluehost and Hostinger are popular choices known for their reliability and user-friendly interfaces. Make sure to choose a plan that aligns with your website's requirements.
Step 2: Back Up Your Website Files
Before making any changes, it’s essential to back up your entire website. This includes all files, databases, and configurations. You can usually do this through your current hosting control panel or by using FTP (File Transfer Protocol) clients like FileZilla.
Step 3: Export Your Database (if applicable)
If your website uses a database (like WordPress), you’ll need to export it. This is typically done using tools like phpMyAdmin:
- Log into phpMyAdmin on your current host.
- Select the database you want to export.
- Click on the "Export" tab and choose the export method (Quick or Custom).
- Download the SQL file to your local computer.
Step 4: Create a New Database
On your new hosting account, create a new database where you will import your data:
- Log into the control panel of your new host.
- Navigate to the database section (often labeled as MySQL Databases).
- Create a new database and note down the database name, username, and password.
Step 5: Import Your Database
Now it’s time to import the database you exported earlier:
- Log into phpMyAdmin on your new host.
- Select the newly created database.
- Click on the "Import" tab.
- Upload the SQL file you downloaded from your old host.
Step 6: Modify Your Website's Files
If necessary, update any configuration files (like wp-config.php for
WordPress) to reflect the new database details (database name, username, password).
Step 7: Upload Your Website's Files
Using an FTP client like FileZilla:
- Connect to your new hosting account.
- Upload all the files from your local backup to the root directory of your new host.
Step 8: Test Your Website
Before updating DNS settings, test your website on the new server by modifying your local hosts file or accessing it via a temporary URL provided by your new host (if available). Check for broken links or missing content.
Step 9: Update DNS Settings
Once everything is functioning correctly on the new host:
- Log into your domain registrar account.
- Update the nameservers to point to those provided by your new hosting provider (e.g., ns1.yournewhost.com).
- Save changes and allow time for DNS propagation (usually up to 48 hours).
Web Hosting Migration Tools
1. BlogVault
BlogVault is a popular WordPress migration tool that has been trusted for nearly a decade. It offers seamless migration with minimal downtime and is particularly user-friendly.
- Key Features:
- URL Rewrites: Automatically updates URLs during migration.
- Backup Options: Provides backup solutions along with migration.
- One-Click Migration: Simplifies the migration process into a few easy steps.
- Pros:
- No downtime during migration.
- Beginner-friendly interface.
- Cons:
- Cannot migrate local websites to an online server.
2. Duplicator
Duplicator is another effective tool for migrating WordPress sites. It allows users to create a package of their site, which can then be moved to a new location.
- Key Features:
- Staging and Merging: Facilitates staging sites and merging changes.
- Backup Capability: Offers backup options during the migration process.
- Pros:
- Simple to use for both local and live site migrations.
- Cons:
- May require some technical knowledge for optimal use.
3. All-in-One WP Migration
This tool focuses solely on the migration aspect, making it one of the most straightforward options available.
- Key Features:
- Drag-and-Drop Functionality: Easily export and import your site.
- No Size Limitations: Handles large sites without issues.
- Pros:
- User-friendly interface.
- Quick and efficient migrations.
4. WP Migrate DB
This plugin is tailored for developers who need advanced database migration features. While the free version only migrates databases, the pro version allows full site migrations.
- Key Features:
- Database Backup: Backs up databases before and after migration.
- Push and Pull Options: Allows easy movement between local and live sites.
- Pros:
- Ideal for developers needing granular control over database migrations.
5. BackupBuddy
BackupBuddy not only helps with backups but also facilitates migrations from localhost to live servers or between hosts.
- Key Features:
- ImportBuddy Tool: Manages URL changes and file paths during migration.
- Pros:
- Comprehensive backup and migration solution.
- Cons:
- Steeper learning curve compared to other plugins.
6. BackupGuard
BackupGuard is primarily a backup plugin but also supports migrations effectively with an easy-to-use interface.
- Key Features:
- Supports serialized data changes during migration.
- Pros:
- Good for beginners needing basic migration capabilities.
- Cons:
- Limited advanced features compared to dedicated migration plugins.
How to Migrate Your Website Using These Tools?
When migrating your website using these tools, follow these general steps:
- Choose Your Migration Tool: Select one of the tools mentioned above based on your needs (e.g., BlogVault for ease of use or Duplicator for more control).
- Install the Plugin on Your Current Site: For WordPress sites, install your chosen plugin through the WordPress dashboard.
- Create a Backup of Your Website: Use the plugin to back up your website files and database before starting the migration process.
- Initiate the Migration Process: Follow the plugin’s instructions to export your site data. This usually involves creating a package that includes all necessary files and databases.
- Set Up Your New Hosting Environment: Ensure that your new hosting account is ready, including creating any necessary databases if required by your chosen tool.
- Upload Your Website Files to the New Host: Use the plugin’s import feature or manually upload files via FTP if using a tool like Duplicator or BackupBuddy.
- Test Your Site on the New Host: Before updating DNS settings, test your site thoroughly to ensure everything functions correctly in its new environment.
- Update DNS Settings: Once you confirm that everything works properly, update your domain's DNS settings to point to your new hosting provider’s servers.
- Monitor Site Performance Post-Migration: After the switch, keep an eye on performance metrics and ensure that all functionalities are working as expected.
IX. Future Trends in Web Hosting
Cloud Hosting Advancements
Cloud hosting has revolutionized the way websites are hosted and managed. Unlike traditional hosting, which relies on a single server, cloud hosting utilizes a network of servers to distribute resources and improve reliability. As we move forward, several advancements in cloud hosting are expected:
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Solutions: Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to optimize performance and avoid vendor lock-in. This approach allows organizations to use a combination of public and private clouds for different workloads, enhancing flexibility and security while improving resource allocation.
- Edge Computing Integration: Edge computing brings data processing closer to the end-user by utilizing decentralized servers located at the network's edge. This reduces latency and enhances the performance of applications by ensuring faster data retrieval. As demand for real-time data processing grows, edge computing will become a critical component of cloud hosting solutions.
- Increased Automation: The integration of AI and machine learning into cloud hosting will lead to more automated management processes. This includes automated scaling based on traffic demands, predictive analytics for resource allocation, and enhanced security measures through real-time threat detection
Future of Cloud Hosting
The future of cloud hosting looks promising as technological innovations continue to evolve. Here are some anticipated changes:
- Enhanced Security Protocols: With the rise in cyber threats, cloud hosting providers will focus on implementing advanced security measures such as multi-factor authentication, automated threat detection, and robust encryption methods to protect user data.
- Sustainability Initiatives: As environmental concerns grow, many hosting providers will adopt green practices by utilizing renewable energy sources and optimizing data center efficiency. This shift toward sustainable solutions will cater to eco-conscious businesses.
- 5G Integration: The rollout of 5G technology will significantly impact cloud hosting by enabling faster data transfer speeds and lower latency. This advancement will enhance user experiences for applications requiring real-time interactions, such as gaming and video streaming.
Cloud Hosting Technologies
Several technologies are driving the evolution of cloud hosting:
- Containerization: Technologies like Docker and Kubernetes allow developers to package applications into containers that can be deployed across various environments seamlessly. This enhances scalability and resource utilization while simplifying management processes.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless architecture allows developers to build applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. This model automatically scales resources based on demand, reducing costs and improving deployment speed.
- Blockchain Technology: The decentralized nature of blockchain can enhance security in cloud hosting by providing transparent data storage solutions that ensure data integrity and reduce vulnerabilities.
Serverless Architecture in Hosting
Serverless architecture is gaining traction as businesses seek more efficient ways to deploy applications without the overhead of managing servers. Here’s why it’s becoming a popular choice:
- Instant Scalability: Serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on traffic demands, allowing businesses to handle sudden spikes in usage without manual intervention.
- Cost Efficiency: With serverless architecture, you only pay for the resources you use rather than maintaining dedicated servers that may remain underutilized during low traffic periods.
- Faster Development Cycles: Developers can focus on writing code without worrying about server management tasks. This leads to quicker deployment times and increased productivity.
- Improved Performance: Serverless computing optimizes resource allocation, resulting in faster code execution and reduced latency for end-users
Green Web Hosting
Green web hosting is becoming increasingly important as businesses and individuals seek to minimize their environmental impact while maintaining a robust online presence.
Let’s explore what green hosting is, highlight some eco-friendly hosting providers, and identify the best options available.
What is Green Hosting?
Green web hosting refers to web hosting services that are environmentally friendly. These providers utilize renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to operate their data centers, significantly reducing their carbon footprint.
Many green hosting companies also engage in initiatives like purchasing Renewable Energy Certificacloud hostingtes (RECs) or Carbon Offset Certificates (VERs) to compensate for their energy consumption.
The goal of green hosting is to provide high-quality services while actively contributing to environmental sustainability. This is achieved through practices like:
- Using renewable energy: Hosting companies may generate their own energy or purchase it from certified green energy suppliers.
- Energy-efficient hardware: Utilizing modern, energy-efficient servers and cooling systems to minimize electricity usage.
- Carbon offsetting: Investing in projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such as tree planting initiatives.
By choosing green hosting, businesses can reduce their ecological impact while still benefiting from reliable and efficient web services.
Eco-Friendly Hosting Providers
Several hosting providers stand out for their commitment to eco-friendly practices:
- GreenGeeks: This provider is well-known for its commitment to sustainability, offering 300% renewable energy for all its services. GreenGeeks invests in wind energy credits to offset its energy usage, ensuring a positive environmental impact.
- HostPapa: HostPapa utilizes 100% renewable energy to power its data centers and offers various eco-friendly hosting solutions. They also provide a range of features such as free domain registration and website builders.
- A2 Hosting: A2 Hosting has a strong focus on green initiatives, utilizing renewable energy sources and offering carbon-neutral hosting solutions. They also prioritize performance with their Turbo Servers for faster load times.
- Hostwoody: An affordable option that uses 100% renewable energy, Hostwoody provides eco-friendly web hosting at competitive prices while emphasizing customer support and user-friendly services.
Best Green Web Hosting
When selecting the best green web hosting provider, consider factors such as reliability, performance, customer support, and commitment to sustainability. Here are some of the top choices:
| Provider | Renewable Energy Commitment | Key Features | Visit Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| GreenGeeks | 300% renewable energy | Eco-friendly practices, unlimited bandwidth | Visit Website |
| HostPapa | 100% renewable energy | Free domain registration, website builder | Visit Website |
| A2 Hosting | Carbon-neutral hosting | Turbo Servers for speed, developer-friendly tools | Visit Website |
| Hostwoody | 100% renewable energy | Affordable plans, user-friendly website builder | Visit Website |
AI and Machine Learning in Hosting
The integration of AI and machine learning into web hosting is transforming the industry, enhancing performance, security, and user experience. As technology evolves, hosting providers are leveraging these advancements to deliver smarter, more efficient services.
Here’s an overview of how AI is used in hosting, the role of machine learning, and some AI-powered hosting features.
How AI is Used in Hosting
AI is revolutionizing web hosting by automating various processes and improving overall efficiency. Here are some key applications:
- Server Management: AI algorithms can monitor server performance in real-time, making automatic adjustments to optimize resource allocation. This proactive management helps reduce downtime and improve website speed by ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently based on current demand.
- Predictive Maintenance: Instead of waiting for hardware failures or crashes, AI can predict potential issues before they occur. By analyzing patterns and historical data, AI tools can identify when a server might fail and initiate maintenance to prevent outages.
- Load Balancing: During traffic spikes, AI can intelligently distribute user requests across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This ensures faster load times and enhances user experience during peak usage periods.
- Security Enhancements: AI plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating security threats in real-time. By analyzing traffic patterns and detecting anomalies, AI can proactively respond to potential cyberattacks, helping to secure websites against unauthorized access
Machine Learning in Web Hosting
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. In web hosting, machine learning contributes significantly to:
- Resource Optimization: ML algorithms analyze usage patterns and predict future resource needs, allowing hosting providers to allocate resources dynamically based on anticipated traffic demands. This leads to better performance and cost efficiency.
- User Behavior Analysis: By examining user interactions with websites, machine learning can help hosting companies understand customer preferences and tailor services accordingly. This analysis can enhance customer satisfaction by providing personalized experiences.
- Automated Reporting: Machine learning can generate detailed reports by analyzing long-term data trends related to server performance and user behavior. These insights help hosting providers make informed decisions about infrastructure improvements
AI-Powered Hosting Features
AI-powered hosting solutions offer several features that enhance the overall hosting experience:
- Automated Customer Support: Many hosting providers now use AI chatbots for customer support, providing instant responses to common queries 24/7. This reduces wait times for customers and allows human support staff to focus on more complex issues.
- Intelligent Resource Allocation: AI systems can automatically adjust server resources based on real-time analysis of traffic loads and application demands, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: AI-driven security measures include real-time threat detection and automated responses to potential breaches. These systems continuously learn from new threats, improving their effectiveness over time.
- Self-Healing Capabilities: Some advanced hosting solutions incorporate self-healing features powered by AI that monitor systems for potential issues and automatically resolve them before they escalate into significant problems
Conclusion
In conclusion, web hosting is a multifaceted domain that encompasses various types, technologies, and features designed to support the diverse needs of websites.
Understanding the fundamentals of web hosting—from what it is and how it works to its critical importance for online presence—is essential for anyone looking to establish or manage a website.
The exploration of different hosting types, such as shared, VPS, dedicated, and cloud hosting, highlights the importance of choosing the right solution based on specific requirements and budget considerations.
As we move forward in an increasingly digital world, advanced technologies like AI and machine learning are transforming web hosting. These innovations enhance performance through intelligent resource allocation, predictive maintenance, and automated security measures, ensuring that websites run smoothly even during peak traffic times.
Additionally, the rise of green web hosting reflects a growing awareness of environmental sustainability within the industry, allowing users to host their websites responsibly.
Moreover, understanding the significance of performance optimization techniques—such as caching, content delivery networks (CDNs), and server management—can dramatically improve user experience and site speed.
As businesses adapt to these trends and technologies, they can leverage the benefits of modern web hosting solutions to create efficient, secure, and scalable online platforms.Ultimately, the future of web hosting lies in continuous improvement and adaptation to new challenges.
By staying informed about emerging trends and best practices in web hosting, businesses can ensure they remain competitive in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Whether you are just starting or looking to migrate to a more robust solution, investing time in understanding web hosting will pay dividends in achieving your online goals.





